North America News
US Stocks Plummet as Hedge Funds Liquidate Positions
The US stock market experienced a brutal sell-off on Thursday, with hedge fund favorites like Netflix, Vistra, Constellation, Broadcom, and GE Vernova plunging.
🔹 Key Factors Behind the Sell-Off:
- Hedge Fund Liquidations: The sharp declines in popular stocks suggest deleveraging, as funds reposition or reduce risk.
- USMCA Tariff Confusion: Trump’s tariff exemptions for Mexico provided some relief, but uncertainty lingers.
- Tech Stocks Under Pressure: The Nasdaq closed below its 200-day MA, a bearish technical signal.
- Upcoming Jobs Report: The February Nonfarm Payrolls report (Friday) is a crucial indicator of economic strength.
🔹 Market Performance:
- S&P 500: -1.8% (closed at 5738.52)
- Nasdaq Composite: -2.6% (closed at 18392)
- Dow Jones: -1.0%
- Russell 2000: -1.5%
🔹 Key Technical Levels:
- S&P 500 briefly fell below its 200-day MA (5730.77) but managed to close above it.
- Nasdaq’s close below its 200-day MA signals further downside risk.
Atlanta Fed Raises GDPNow Estimate to -2.4% for Q1
The Atlanta Fed GDPNow model raised its Q1 2025 growth estimate to -2.4% from -2.8% earlier this week.
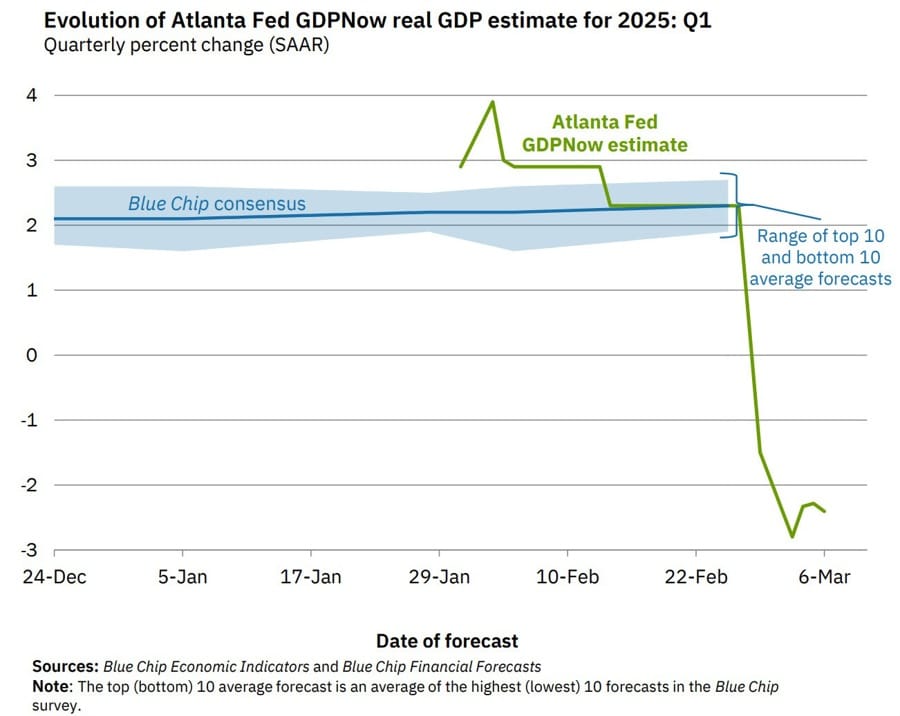
🔹 Key Drivers:
- Auto Sales: Helped improve GDP estimate from -2.8% to -2.3%.
- ISM Services Index: Had neutral impact on estimates.
- Trade & Wholesale Data: Slight drag on overall growth.
🔹 What This Means:
- Still in contraction: A -2.4% growth rate signals economic slowdown.
- Consumer spending remains weak: This aligns with recent retail and business sentiment reports.
- Fed policy implications: Could increase pressure for rate cuts to support the economy.
In their own words:
The GDPNow model estimate for real GDP growth (seasonally adjusted annual rate) in the first quarter of 2025 is -2.4 percent on March 6, up from -2.8 percent on March 3. After recent releases from the Institute for Supply Management, the US Bureau of Economic Analysis, and the US Census Bureau, the nowcasts of first-quarter real personal consumption expenditures growth and real gross private domestic investment growth increased from 0.0 percent and 2.5 percent, respectively, to 0.4 percent and 4.8 percent, while the nowcast of the contribution of net exports to first-quarter real GDP growth fell from -3.57 percentage points to -3.84 percentage points.
US Trade Deficit Hits Record High of $131.4 Billion in January Amid Surging Imports
The US international trade balance for January 2025 widened to a record deficit of $131.4 billion, exceeding estimates of -$127.4 billion and significantly higher than December’s revised -$98.4 billion.
Key Figures:
- Exports: $269.8B (+3.3B from December)
- Imports: $401.2B (+36.6B from December)
- Goods Deficit: -$156.8B (previous record: -$122B)
- Services Surplus: +$25.4B (+0.2B from December)
- Year-over-Year Deficit Growth: +96.5%
- Year-over-Year Import Growth: +23.1%
- Year-over-Year Export Growth: +4.1%
This marks the largest-ever monthly trade deficit for the US, fueled by an unprecedented surge in imports, particularly in industrial supplies, finished metals, and consumer electronics.
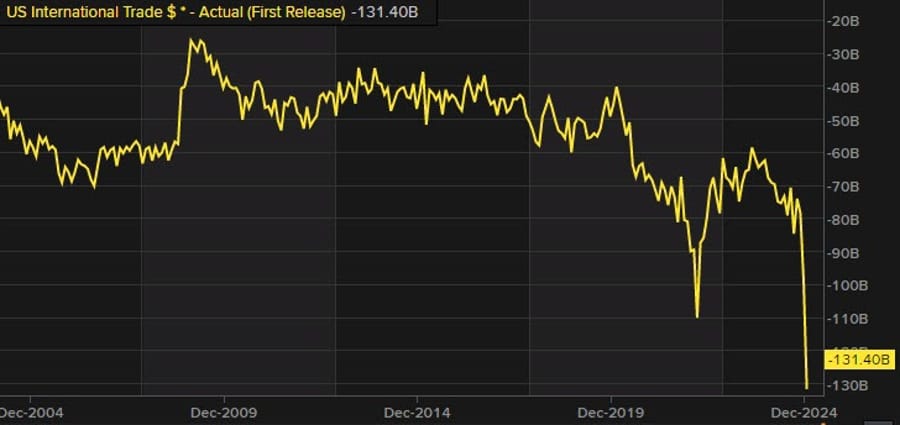
Breakdown of US Trade Data
Imports Surge Across Key Sectors
Total goods imports rose by $36.2B to $329.5B, driven by:
- Industrial supplies & materials: +$23.1B
- Finished metal shapes: +$20.5B
- Consumer goods: +$6.0B
- Pharmaceuticals: +$5.2B
- Cell phones & household goods: +$1.2B
- Capital goods: +$4.6B
- Computers: +$3.0B
- Computer accessories: +$1.2B
- Telecom equipment: +$1.1B
- Services imports also increased: +$0.4B
- Intellectual property charges: +$0.2B
- Other business services: +$0.1B
The sharp increase in imports reflects strong US demand for technology, pharmaceuticals, and industrial materials, likely exacerbated by tariff concerns and front-loading ahead of potential new trade restrictions.
Exports Rise But Lag Behind Import Growth
Total exports rose $2.7B to $172.8B, led by:
- Capital goods: +$4.2B
- Civilian aircraft: +$1.1B
- Semiconductors: +$0.7B
- Computers: +$0.5B
- Consumer goods: +$1.7B
- Pharmaceuticals: +$0.8B
- Jewelry: +$0.6B
- Services exports rose +$0.6B to $97.0B
- Financial services: +$0.2B
- Telecom & information services: +$0.1B
- Transport services: +$0.1B
However, food exports fell -$1.0B, with soybeans declining -$0.8B, reflecting weaker global demand.
Despite the increase in exports, the rapid growth in imports far outpaced outbound trade, leading to a record trade gap.
US Trade Deficit by Country: Key Imbalances Grow
The US posted record deficits with multiple trade partners, fueling trade policy concerns.
Largest Deficits (Billions $):
- China: -$29.7B (remains the largest trade imbalance)
- European Union: -$25.5B
- Switzerland: -$22.8B (↑$9.8B, largest single-month jump)
- Mexico: -$15.5B
- Ireland: -$12.4B (↑$6.2B, driven by tech imports)
- Vietnam: -$11.9B
- Canada: -$11.3B
- Germany: -$7.6B
- Taiwan: -$7.5B
- Japan: -$7.4B
Switzerland’s surging luxury goods and pharmaceutical exports pushed its trade surplus with the US to nearly match that of the entire EU. Meanwhile, Ireland’s trade deficit soared due to a 6.2B increase in US imports of tech components.
These growing trade imbalances provide further justification for Trump’s aggressive tariff stance, particularly against Canada, Mexico, and China.
Market and Policy Implications
1️⃣ Trump’s Tariff Strategy Gains Momentum
The massive trade deficit will likely reinforce Trump’s argument for aggressive trade measures.
- With Mexico and Canada both running large deficits, expect further pressure on auto and manufacturing tariffs.
- China’s dominance as the largest trade gap holder could provoke even harsher restrictions.
- The record Swiss surplus may also trigger new scrutiny on pharmaceutical imports.
2️⃣ Impact on Federal Reserve and Inflation
- Surging imports suggest strong domestic demand, which could keep inflation elevated.
- The weaker-than-expected export growth could weigh on US GDP, further complicating Fed policy decisions.
- A strong US dollar could continue widening the trade deficit, unless countered by new tariffs or a weaker currency policy.
3️⃣ Risks to Corporate Earnings and Supply Chains
- Companies reliant on imported inputs (tech, pharmaceuticals, industrial metals) may face higher costs if tariffs escalate.
- Export-heavy firms could struggle as rising global trade tensions limit demand for US goods.
- The tariff war could disrupt supply chains, particularly for automakers, tech firms, and energy producers.
US Jobless Claims Fall to 221K, Lower Than Expected
The latest weekly jobless claims data showed:
- Initial claims: 221K (vs. 235K expected).
- Prior week: 242K (revised to 224K).
- Continuing claims: 1.897M (vs. 1.880M expected).
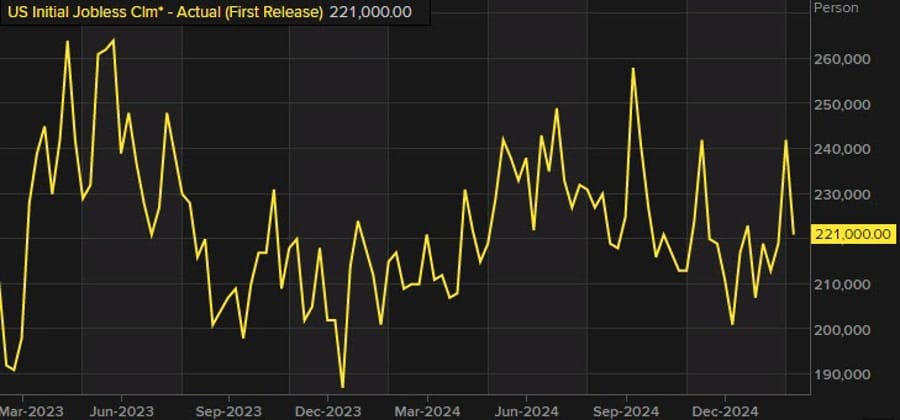
The modest decline in jobless claims suggests the labor market remains resilient, even amid growing economic uncertainty.
US Q4 Labor Costs Rise 2.2%, Below Expectations
The US Q4 unit labor costs rose 2.2%, missing the 3.0% forecast.
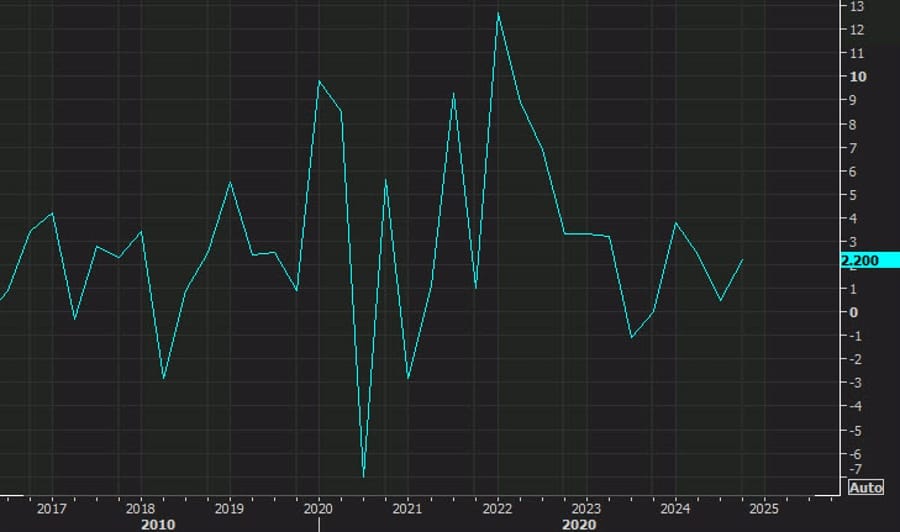
- Productivity increased +1.5% (vs. +1.2% prelim).
- Lower labor costs suggest wage inflation may be cooling, which could ease pressure on the Fed.
The data suggests a more balanced labor market, but the Fed will be watching upcoming inflation trends closely.
US Wholesale Inventories Jump 0.8% in January, But Sales Decline
US wholesale inventories rose 0.8%, slightly above expectations (0.7%), but sales fell -1.3%, missing forecasts for a +1.0% increase.
- Previous month’s sales revised up to +1.4%.
- Rising inventories could indicate weakening demand, which could weigh on future production.
The drop in sales signals potential softness in consumer and business spending, which could impact future economic growth.
US February Job Cuts Surge 245% to Highest Since 2020
The Challenger Layoffs report showed 172,017 job cuts in February, a massive jump from 49,790 in January.
- The increase is 245% higher than February 2024, making it the worst month for layoffs since July 2020.
- Federal government job cuts accounted for over 62,000 of the total, linked to budget reductions and Trump’s Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) initiative.
- Technology and retail sectors also saw sharp increases in layoffs.
This raises concerns about the health of the U.S. labor market, especially as consumer confidence weakens.

Fed’s Waller: Seeing some signs of softer data
- Comments from the Fed Governor on the economic outlook
- Not all tariffs are passed through
- We have to respond to hard data
- Waiting to see if weakness in soft data shows up in broader statistics
- Doesn’t see a case for a March rate cut
- Could see rate cuts after the March meeting
- It does sound like we’re getting the band back together on ‘team transitory’ regarding tariff impacts
- It is very hard to eat a 25% tariff
- I’m particularly interested to market pricing on inflation expectations
- I don’t particularly pay attention to consumer inflation expectation surveys
Trump Considering NATO Policy Shift – Would Not Defend Members Below Spending Targets
NBC News reports that Trump is weighing a major shift in NATO policy, signaling that the US may not defend NATO allies who fail to meet defense spending requirements.
🔹 Policy Under Consideration:
- US would prioritize defending NATO members that meet defense spending thresholds (currently 2% of GDP).
- Countries below the threshold may receive reduced military support or, in extreme cases, no direct US defense commitments.
This potential policy shift could undermine NATO unity, particularly in Europe, where many allies still lag behind defense spending targets.
🔹 Potential Impacts:
- Increased European defense spending: Nations may accelerate military budgets to ensure continued US protection.
- Strained US-Europe relations: Allies that struggle to meet the spending threshold may push back diplomatically.
- Russia-China geopolitical implications: NATO’s perceived weakening could embolden adversaries.
This controversial stance aligns with Trump’s long-standing criticism of NATO’s financial burden on the US and could reshape global security alliances.
Here is the report.
US Treasury Secretary Bessent: “Iran’s Economy Will Collapse”
US Treasury Secretary Bobby Bessent issued aggressive remarks against Iran, signaling severe new economic sanctions aimed at shutting down Iran’s oil sector and drone manufacturing capabilities.
🔹 Bessent’s Comments:
“We are going to shut down Iran’s oil sector and drone manufacturing capabilities. We will close Iran’s access to the international financial system. Sanctions will be used explicitly and aggressively for a maximum impact. If economic security is national security, Iran will have neither.”
🔹 Implications for Global Markets:
- Oil prices may surge if Iranian supply is significantly disrupted.
- Iran’s economy faces collapse as US sanctions tighten financial restrictions.
- Increased geopolitical tensions in the Middle East.
This escalation in US-Iran tensions is a critical risk factor for energy markets and global security.
Trump Grants Tariff Exemptions to Mexico, Additional Exemptions Expected Later Today
Trump Officially Confirms Mexico’s Tariff Exemption Until April 2
President Donald Trump announced that Mexico will not be subject to new tariffs on USMCA-covered goods until April 2, confirming earlier statements from Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick.
🔹 Trump’s Statement:
“After speaking with President Claudia Sheinbaum of Mexico, I have agreed that Mexico will not be required to pay tariffs on anything that falls under the USMCA Agreement. This Agreement is until April 2nd. I did this as an accommodation, and out of respect for, President Sheinbaum. Our relationship has been a very good one, and we are working hard, together, on the Border, both in terms of stopping Illegal Aliens from entering the United States and, likewise, stopping Fentanyl.”
This decision marks a temporary relief for Mexico as the White House assesses future reciprocal tariff measures for April 2 and beyond.
Additional Tariff Exemptions Coming Later Today
According to Fox Business reporter Edward Lawrence, a White House official has confirmed that more tariff exemptions will be announced this afternoon, beyond just Mexico.
🔹 Key Sectors to Watch for Exemptions:
- Automobiles & Parts: Auto manufacturers have been lobbying for exclusions.
- Industrial Goods & Machinery: Companies in these sectors rely on tariff-free supply chains.
- Agriculture: Farmers are already facing pressure from retaliatory tariffs from Canada & China.
These upcoming announcements could have significant implications for stock markets and international trade.
Lutnick: Tariff Reprieve Coming Today for USMCA-Compliant Goods
US Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick hinted at a tariff reprieve for goods compliant with the USMCA trade agreement.
- A delay on tariffs is likely to be announced today.
- It will likely cover all USMCA-compliant goods, not just automakers.
- If Canada and Mexico make further concessions, broader tariff relief could be considered by April 2.
While this signals a temporary pause in escalating trade tensions, the US is still committed to enforcing reciprocal tariffs if demands are not met.
Fed’s Harker: Economy Looks “Okay,” But Risks Are Growing
Philadelphia Fed President Patrick Harker provided a mixed assessment of the US economy.
- Consumer and business confidence is weakening, which is concerning.
- Declining inflation pressure is at risk of reversing.
- Growing concern over US government deficits and their long-term implications.
While Harker did not hint at any immediate policy shifts, his comments suggest the Fed remains cautious about economic threats.
BlackRock-Led Consortium Acquires Majority Stake in Panama Ports Business
A U.S.-led group, led by BlackRock, secured a 90% stake in Panama Ports Company, valued at $22.8 billion.
- The deal includes key strategic assets at the Panama Canal, reinforcing U.S. influence over a major global trade route.
- Trump hailed the deal as a move to “reclaim” the Panama Canal from Chinese influence.
- However, Panama’s President Jose Raul Mulino dismissed these claims, reaffirming that the canal remains under Panama’s control.
Fed’s Perli: Balance Sheet Drawdown Has Been Smooth
Roberto Perli, manager of the Fed’s System Open Market Account (SOMA), commented on quantitative tightening (QT):
- If the Fed pauses QT, it wouldn’t change the ultimate goal.
- The Fed’s balance sheet currently stands at $6.8 trillion.
- Financial system reserves remain abundant, and the repo market is normalizing.
- Potential SRF (Standing Repo Facility) operations could return at quarter-end to support liquidity.
These remarks suggest that the Fed remains in control of its tightening cycle, but is prepared to adjust if necessary.
Mexican President Sheinbaum Confirms Tariff Agreement
Mexican President Claudia Sheinbaum publicly confirmed the agreement with Trump, expressing gratitude for the “excellent and respectful call” between the two leaders.
🔹 Sheinbaum’s Statement:
“We will continue working together, particularly on issues of migration and security, which include reducing the illegal crossing of fentanyl into the United States, as well as weapons into Mexico. As President Trump mentions, Mexico will not be required to pay tariffs on all those products within the USMCA. This agreement is until April 2, when the United States will announce reciprocal tariffs for all countries.”
Sheinbaum’s focus on migration and security cooperation suggests that these topics played a key role in securing Mexico’s exemption.
Trudeau: Canada Continues Talks with US, But Trade War Is Far from Over
Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau made it clear that tariffs imposed by the US remain a major economic concern.
- “We will continue to be in a trade war that was launched by the United States for the foreseeable future.”
- “As long as there are tariffs on Canada from the US that are completely unjustified, we will be responding strongly.”
- Said he had a “colorful and substantive” conversation with Trump on Wednesday.
Trudeau’s firm stance suggests Canada will not back down until the US removes tariffs, prolonging trade tensions between the two nations.
Canada’s January Trade Surplus Soars to C$3.97 Billion, Crushing Expectations
Canada posted a trade surplus of C$3.97 billion in January, far exceeding expectations of C$1.28 billion.
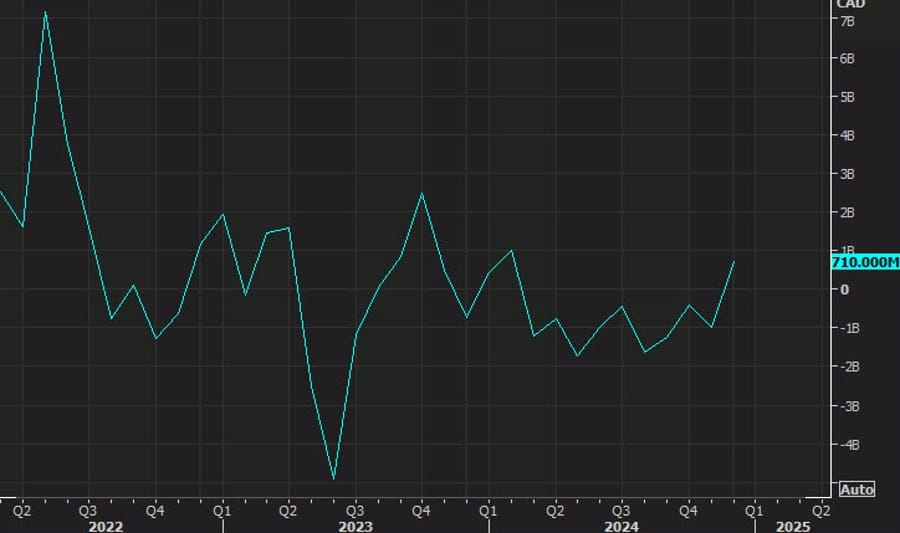
- Exports jumped, driven by:
- Motor vehicles and parts (+12.5%), with passenger car exports surging 17.1%.
- Consumer goods (+7.8%) and industrial machinery (+12.6%) also contributed to the gains.
- Imports remained stable, showing resilience despite trade uncertainties.
The strong trade balance reflects Canada’s ability to navigate tariff headwinds for now, but continued uncertainty over US trade policy remains a risk.
Canada May Use Oil and Gas Exports as Leverage in U.S. Tariff Negotiations
Canada’s Foreign Minister Mélanie Joly suggested that Canada could use its energy exports as a bargaining tool against U.S. tariffs.
- Canada has already pledged C$155 billion in retaliatory tariffs.
- While tariffs on U.S. goods are planned, restrictions on energy exports have not been proposed—yet.
- Canada currently exports 4 million barrels of oil per day to the U.S., representing 90% of its total crude exports.
If tensions escalate, oil and gas could become a critical point in Canada’s countermeasures.
Commodities News
Gold Stalls Near $2,910 as Investors Await Jobs Report
Gold remained firm near $2,918, consolidating ahead of Friday’s US Nonfarm Payrolls report.
🔹 Gold Market Dynamics:
- Profit-taking capped gains after a three-day rally.
- Higher bond yields made non-yielding gold less attractive.
- Atlanta Fed GDPNow: Revised Q1 GDP forecast to -2.4% from -2.8%, fueling recession fears.
- Retaliatory Tariffs: Canada & China’s response to Trump’s tariffs added geopolitical risk, supporting gold.
🔹 US Economic Data Recap:
- Challenger Job Cuts: Surged to 172K, highest since 2020.
- Initial Jobless Claims: Fell to 221K, suggesting labor market resilience.
Takeaway: Gold is stabilizing ahead of the jobs report but remains supported by recession fears and trade war risks.
Oil Prices Rebound Slightly After Sharp Sell-Off
Crude oil settled at $66.36, up just $0.05 (+0.08%), as supply concerns and weakening demand continued to weigh on the market.
🔹 Key Factors Impacting Oil Prices:
- Rising US Inventories: The EIA reported a 3.6-million-barrel increase, higher than expected.
- OPEC+ Supply Increase: The cartel plans to unwind 2.2 million bpd of production cuts over the next 18 months.
- US Output at Record Highs: 13.51 million bpd production last week, signaling strong non-OPEC supply growth.
- Demand Concerns: Economic slowdown fears and trade war escalation could hurt oil demand.
📌 Takeaway: Bearish fundamentals continue to dominate oil markets. Any recovery will require demand stabilization or geopolitical shocks.

Copper Soars on Trump’s 25% Tariff Proposal
Copper rallied 5% after Trump proposed a 25% tariff on copper imports, leading to a COMEX/LME price arbitrage spike to $1,000/t.
🔹 China Responds:
- China’s National Development and Reform Commission pledged production cuts in the steel & oil industry.
- China’s steel output remains over 1 billion tonnes, despite Beijing’s push to cut capacity.
European Gas Prices Volatile on Russia Supply Speculation
European natural gas prices dropped 4.5%, as investors speculated on a possible return of Russian pipeline gas under a peace deal.
🔹 Key Market Drivers:
- EU Delayed Fossil Fuel Phase-Out Plan, seen as a softening stance on Russian energy imports.
- EU Storage Targets Flexibility: Countries aim for 90% capacity by November, but adjustments may be made.
Trump Reportedly Planning to Disrupt Iran’s Oil Exports
Reuters reports that President Trump is considering a plan to block Iranian oil shipments, escalating tensions in the Middle East.
- The plan involves halting and inspecting Iranian oil tankers at critical shipping lanes.
- This would disrupt Iran’s ability to export crude oil, further pressuring its economy.
- The move is part of Trump’s “maximum pressure” campaign against Iran.
Oil markets are closely watching developments, as any major disruption could cause a significant spike in global oil prices.
Europe News
ECB Cuts Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points, Signals More Easing Ahead
The European Central Bank (ECB) announced a 25 basis point rate cut, lowering its deposit facility rate to 2.50%, as expected.
- Key rate adjustments:
- Deposit facility rate: 2.50% (prior: 2.75%)
- Main refinancing rate: 2.65% (prior: 2.90%)
- Marginal lending facility: 2.90% (prior: 3.15%)
Key Takeaways from the ECB Decision:
- Monetary policy is becoming less restrictive, making borrowing cheaper for households and businesses.
- The disinflation process is on track, but energy prices remain a risk.
- Economic growth forecasts have been downgraded, with GDP expected to grow 0.9% in 2025, 1.2% in 2026, and 1.3% in 2027.
- Trade policy uncertainty and weak investment continue to weigh on growth.
- ECB remains data-dependent and will assess rate cuts on a meeting-by-meeting basis.
The ECB is signaling a more cautious easing cycle, avoiding a pre-committed path while acknowledging ongoing economic challenges.
ECB’s Lagarde Warns of Fragile Consumer Confidence and Investment Risks
Christine Lagarde, President of the ECB, highlighted concerns over weak investment sentiment and fragile consumer confidence.
- Manufacturing remains a drag, while services are resilient.
- Uncertainty is holding back business investment more than expected.
- Trade tensions pose a major risk to growth, particularly weighing on exports.
- Defense and infrastructure spending could fuel inflation, complicating future policy decisions.
- Geopolitical uncertainty remains high, creating two-sided risks for inflation.
Q&A Highlights from Lagarde:
- ECB is moving to a more “evolutionary approach” to policy.
- Increased fiscal spending could provide a boost to growth, but the ECB will monitor its inflation impact.
- Despite market expectations, the ECB is not pre-committing to a specific rate-cutting path.
Lagarde’s remarks underscore the ECB’s delicate balancing act between easing monetary policy and ensuring inflation stays under control.
Eurozone Retail Sales Disappoint, Falling -0.3% in January
The latest data from Eurostat shows that Eurozone retail sales fell -0.3% month-on-month in January, missing expectations of +0.1%.
- Non-food products dropped -0.7%, while automotive fuel sales fell -0.3%.
- Food sales provided a small offset, rising +0.6%.
The data suggests that consumer demand remains weak, raising concerns about whether the European Central Bank (ECB) will be forced to cut rates sooner than expected.

Germany’s Construction Sector Still in Deep Contraction, PMI at 41.2
Germany’s construction PMI fell to 41.2 in February, down from 42.5.
- New orders remain weak, showing little sign of improvement.
- Housing, commercial, and civil engineering projects all remain in contraction.
- Uncertainty over fiscal policies, interest rates, and labor shortages continues to dampen activity.
While Germany’s manufacturing sector is showing some signs of stabilization, construction remains one of the economy’s biggest weak spots.
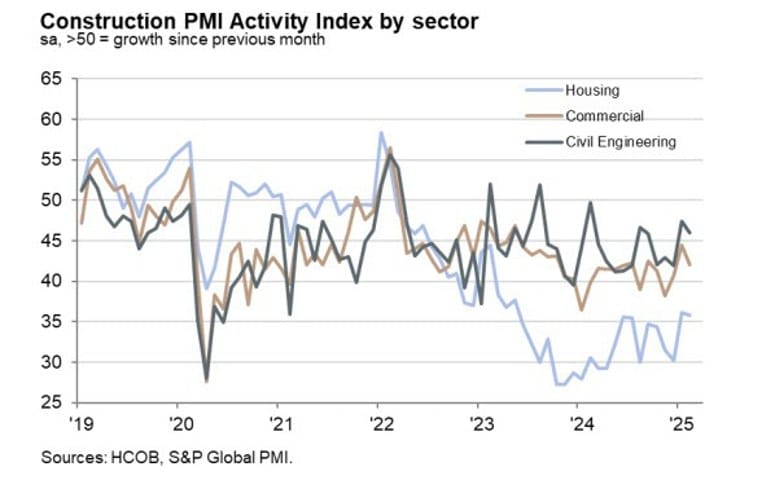
HCOB notes that:
“The construction sector is still far from recovery. After a strong month-on-month increase in the headline PMI in January, companies couldn’t keep up the momentum and reported a faster fall in activity. This drop in performance can be seen in the residential construction sector, commercial real estate, and civil engineering. The recession hits hardest in residential construction and is the least severe in civil engineering. If the newly formed government decides to roll out a comprehensive infrastructure program, it would likely benefit civil engineering the most. However, the economic boost would also help other sectors of the construction industry.
“New orders are still scarce in the construction sector. Since spring 2022, orders have been dropping month after month. Currently, there are no signs that the construction industry will get more orders anytime soon. Against this backdrop, companies continue to cut jobs, with the pace of staff shedding remaining broadly steady for five months.
“Looking ahead, companies are slowly crawling out of the depths of depression. The index of future activity has actually risen to its highest level since February 2022. Although companies, on balance, still think that activity in a year’s time will be lower than it is today, the trend of rising confidence over the past three months shouldn’t be overlooked.
“A glance at the low capacity utilization in the construction sector, evidenced by the increasing availability of subcontractors over the past two years, shows that an economic stimulus package would be particularly effective right now. With low capacity utilization, new orders could be absorbed without significant price increases. In this sense, it’s a good time to kickstart the economy with a government infrastructure program.”
UK Construction PMI Falls to 44.6, Worst in Nearly Five Years
The UK construction sector continues to deteriorate, with the February PMI dropping to 44.6, well below expectations of 49.5.
- The lowest reading since early 2020, with declines in both housing and civil engineering projects.
- Residential building activity fell for a fifth straight month, reaching 39.3, its worst performance since early 2009 (excluding the pandemic crash).
- Rising costs, higher interest rates, and uncertainty over government policies have stifled demand.
This sharp decline raises concerns over the UK’s broader economic outlook, adding pressure on the Bank of England to reassess its rate stance.

S&P Global notes that:
“Sharply declining order books rippled through the UK construction sector in February, which led to accelerated reductions in output volumes, employment and input buying. Weak demand conditions were attributed to entrenched caution among clients, against a backdrop of subdued consumer confidence and lacklustre economic performance.
“Aside from the pandemic, total industry activity decreased at the steepest pace since December 2019. This was led by considerable reductions in residential building and civil engineering work, while a degree of resilience was reported for commercial construction activity. Survey respondents widely cited a lack of new work in the house building segment, due to soft market conditions and the impact of elevated borrowing costs.
“Construction companies remain optimistic overall about their growth prospects for the next 12 months, albeit less so than on average in 2024 amid increasing concerns about the broader UK economic outlook. The were also signs that rising payroll costs and purchasing prices have become a source of anxiety, with the latest increase in overall business expenses the steepest since March 2023.”
Switzerland’s Unemployment Rate Holds at 2.7% for the Third Straight Month
The Swiss jobless rate remained at 2.7% in February, meeting expectations.
- Despite stability, the figure remains above the post-pandemic low of 1.9% from March 2023.
- The labor market remains tight, but global trade uncertainties and rising costs could pressure employment going forward.
Switzerland’s economy remains relatively strong, but potential economic slowdowns in Europe and global trade disputes pose risks.
ECB Sources: April Rate Cut is Now Unlikely
A Reuters report citing ECB sources suggests that the chances of a rate cut in April are declining.
🔹 Key Insights:
- Market expectations: A 43% chance of an April rate cut was already priced in.
- Core inflation concerns: ECB is hesitant to cut too soon as inflation remains above 2% target.
- Interest rate path: 2.5% is unlikely to be the bottom, but the pace of cuts may slow.
🔹 Market Implications:
- Eurozone bonds: Likely to face selling pressure if rate cuts are delayed.
- Euro currency: May strengthen if the ECB holds rates steady, affecting exports.
- Stock markets: Could react negatively if rate cuts are postponed, especially in Germany and France.
Germany’s Lower House to Vote on Debt Brake Reform on March 18
The Bundestag (Germany’s lower house) is set to vote on a key fiscal reform aimed at loosening the debt brake, allowing for more government spending.
- Discussions will begin on March 13, with a vote on March 18.
- Approval requires a two-thirds majority from both the Bundestag and Bundesrat (upper house).
- Current government parties (CDU/CSU and SPD) hold 403 seats but need 86 more votes.
- FDP is unlikely to support the reform, and the Greens remain undecided.
If approved, Germany could unlock billions in new spending for defense, infrastructure, and economic stimulus, potentially boosting growth but increasing debt concerns.
Asia-Pacific & World News
PBOC Governor Pan Hints at Future Rate Cuts and Reserve Requirement Reductions
People’s Bank of China (PBOC) Governor Pan Gongsheng signaled that interest rate and Reserve Requirement Ratio (RRR) cuts will come at an appropriate time.
- PBOC will study and establish new structural monetary policy tools to support growth.
- The bank will also act to prevent exchange rate overshooting risks, ensuring financial stability.
- His remarks align with China’s broader strategy to counter economic headwinds and maintain liquidity in the financial system.
These comments suggest that further monetary easing is on the horizon, but policymakers remain cautious about capital outflows and inflation risks.
PBOC Governor: China’s External Environment Becoming More Complex and Severe
Further remarks from Governor Pan Gongsheng highlight the growing external risks China faces.
- Must strictly prevent risks from external shocks, ensuring economic resilience.
- China has the confidence and ability to maintain FX market stability, likely addressing concerns about yuan depreciation.
- The global trade environment remains uncertain, with U.S. tariffs and geopolitical tensions increasing financial stress.
With China facing slowing growth and ongoing trade disputes, policymakers are preparing stronger interventions to stabilize markets.
China Unveils AI Agent ‘Manus,’ Claims It Outperforms OpenAI Models
China has introduced Manus, a cutting-edge AI agent, claiming it surpasses OpenAI’s models in performance, according to Shanghai Securities News.
- Manus achieved a top score in the GAIA benchmark test, positioning it as a highly advanced general-purpose AI assistant.
- Unlike traditional AI models, Manus is designed not just for generating ideas but also for real-world execution.
- A live demonstration showcased its ability to autonomously write reports, generate tables, and complete complex tasks with customized outputs.
- Its “digital brain” enables independent learning, multi-domain task execution, and advanced problem-solving, making it one of the most sophisticated AI agents developed by China.
Manus is part of China’s broader push to compete with Western AI dominance, with an emphasis on practical applications in government, business, and industry.
Goldman Sachs: Chinese Banks to Undergo Capital Restructuring with RMB500 Billion Bond Issuance
The Chinese government has announced a RMB500 billion ($69 billion) bond issuance to support capital replenishment for major state-owned banks.
- Goldman Sachs previously estimated an issuance of RMB240 billion, but the final figure surpassed expectations while remaining below the RMB1 trillion the market had anticipated.
- The bond issuance aims to strengthen capital reserves, particularly for Postal Savings Bank of China (PSBC), Bank of Communications (BANKCOMM), Bank of China (BOC), and Agricultural Bank of China (ABC).
- Goldman Sachs expects the restructuring to occur in phases, ensuring financial stability without severely impacting earnings per share (EPS) or dividend yields.
This move is part of China’s ongoing efforts to stabilize its financial system as it navigates a complex economic environment.
China Sets Record in Bad Asset Disposals, Shifts Focus to Housing Market
China disposed of RMB3.8 trillion ($530 billion) in non-performing assets in 2024—the highest on record—as authorities worked to clean up financial risks.
- The financial regulator indicated that 2025 will focus on stabilizing the housing market, signaling an intensified effort to support the struggling property sector.
- This underscores Beijing’s broader strategy of maintaining financial stability while addressing real estate and banking challenges.
- Analysts view this as a crucial step in reducing systemic risk, as China continues to manage its economic slowdown and real estate downturn.
PBOC sets USD/ CNY reference rate for today at 7.1692 (vs. estimate at 7.2386)
- PBOC CNY reference rate setting for the trading session ahead.
PBoC injects 104.5bn yuan via 7-Day Reverse Repos at 1.5%
- 215bn mature today
- Net drain is 110.5bn yuan

Australian Trade and Building Approvals Beat Expectations in January
Australia’s latest economic data surprised to the upside, reinforcing economic resilience.
Trade Data (January 2025):
- Exports (MoM): +1.3% (prior +1.2%).
- Imports (MoM): -0.3% (prior +5.9%).
- Trade Balance: AUD 5.62B (expected AUD 5.85B, prior AUD 4.92B).
Building Approvals (January 2025):
- Monthly: +6.3% (expected -0.1%, prior +0.7%).
- Yearly: +21.7% (expected +5.6%, prior +10.1%).
The data suggests Australia’s economy remains resilient, despite global economic headwinds.
TD Bank Forecasts RBA Rate Cuts in May and August 2025
TD Bank expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to cut rates in May and again in August, citing:
- Easing rental inflation, which could reduce broader inflationary pressures.
- Heightened trade uncertainty, pushing bond yields lower and increasing the likelihood of monetary easing.
TD analysts emphasized global trade developments as a key driver of the RBA’s future rate decisions.
Japan’s Largest Labor Union Seeks Record 6.09% Wage Hike for 2025
Japan’s largest union group, Rengo, announced it is seeking an average wage hike of 6.09% for 2025, a significant increase over past years.
- For context:
- 2024 wage hike: 5.25%
- 2023 wage hike: 3.80%
- This surpasses the expected “at least 5%” hike that was seen as necessary for the Bank of Japan (BoJ) to justify further monetary tightening.
- Stronger wage growth supports the BoJ’s inflation targets, making a July interest rate hike more likely.
This increase will further fuel Japan’s economic recovery, reinforcing the BoJ’s push toward policy normalization.
BoJ Ex-Chief Economist: Bank of Japan Policy Rate Could Rise to 2%, Next Hike Likely in July
Toshitaka Sekine, a former Chief Economist at the Bank of Japan, suggested:
- BoJ’s policy rate could rise to 2% under the Taylor Rule framework, assuming inflation remains at 2%.
- A rate hike in May is possible, but July is the more likely scenario.
- The BoJ is not overly concerned with yen depreciation, though a weaker yen could make rate hikes more politically acceptable.
- Repatriation flows may not be significant, given that Japanese households have not dramatically increased exposure to U.S. assets.
Japan’s ‘Mr. Yen’ Mimura Warns of Rising Trade Protectionism
Atsushi Mimura, Japan’s Vice Finance Minister for International Affairs, also known as ‘Mr. Yen,’ noted:
- There is an increasing trend of protectionist policies globally, with tariffs becoming a major issue.
- A balance must be struck between globalization and protecting domestic industries, to avoid a full slide into economic protectionism.
- Japan must navigate U.S. trade tensions carefully, particularly in light of Trump’s recent tariff escalations.
South Korea’s February Inflation Surprises to the Upside, but Slows from January
South Korea’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) for February:
- CPI +2.0% y/y (expected +1.95%, prior +2.2%).
- Month-on-month CPI +0.3% (expected +0.2%).
- Core CPI +1.8% y/y (prior +1.9%).
This suggests inflation remains sticky, though slightly moderating from January levels.
Crypto Market Pulse
Crypto Traders Bet on White House Crypto Summit
The total crypto market cap surged by $175 billion (+6%), with Bitcoin, XRP, and AI tokens leading gains.
🔹 Bitcoin Market Update:
- BTC traded near $89,900, down 2% from a 24-hour peak of $92,800.
- Bitcoin ETFs saw another $38M in outflows, marking the third straight day of selling.
🔹 Altcoin Rally:
- XRP (+4%) broke the $2.50 level, signaling potential for further upside.
- Ethereum (+2%) reclaimed $2,200.
- Chainlink (+11%) touched $20, boosted by its partnership with Trump’s World Liberty Financial (WLFI).
- AI tokens (Near Protocol & Render) surged 9%, outperforming the broader market.
🔹 White House Crypto Summit Sparks Buying:
- Trump’s administration has signaled pro-crypto policies, encouraging investors to bet on regulatory clarity.
- Near Protocol, Render, and Chainlink saw heavy inflows due to AI & DeFi integration speculation.
🔹 Crypto Regulatory Updates:
- New York State Assembly Introduced Bill A05515 to combat crypto fraud, targeting rug pulls & undisclosed token interests.
- Brazil’s Méliuz Allocates 10% of Cash Reserves to Bitcoin, following MicroStrategy’s lead.
- Dubai’s Emirates NBD partnered with Aquanow to launch crypto trading via its Liv X digital banking platform.
Takeaway: The White House Crypto Summit hype is driving market gains, but traders must watch ETF outflows & macroeconomic trends.

SUI Token Surges 10% on Trump’s World Liberty Financial Partnership
The Sui blockchain (SUI) rallied +10% after announcing a partnership with Trump-inspired World Liberty Financial (WLFI).
🔹 Key Details of the Partnership:
- WLFI integrates SUI into its “Macro Strategy” reserve.
- Eric Trump named Web3 Ambassador at WLFI.
- WLFI doubled its Ethereum holdings to 7,100 ETH, signaling strong crypto backing.
Takeaway: Trump-aligned crypto projects are seeing massive inflows—SUI’s surge reflects growing investor interest in politically linked assets.

The Day’s Takeaway
Day’s Takeaway: Key Market Trends & Developments
📊 Market Takeaways: Key Trends to Watch
US Stock Market:
- Tech stocks are vulnerable as hedge funds unwind positions.
- Nasdaq’s break below its 200-day MA is a major warning sign.
- Nonfarm Payrolls on Friday will be a decisive moment for markets.
Oil Prices:
- OPEC+ supply increase & record US output could limit upside potential.
- Bearish sentiment dominates unless demand recovers.
Gold Consolidation:
- Profit-taking is capping upside, but recession fears support gold.
- If job numbers disappoint, gold could test $2,950+.
Crypto Momentum:
- White House Crypto Summit is fueling bullish sentiment.
- Trump-linked crypto projects like SUI & Chainlink are seeing major inflows.
- Bitcoin remains under pressure amid ETF outflows.
Final Thought:
Markets are highly volatile with tech stocks sinking, commodities reacting to tariffs, and crypto surging on regulatory optimism.
- Tomorrow’s NFP data will be a turning point—prepare for more turbulence! 🚨

















