North America News
Tech Rout Pulls NASDAQ Down Over 2% as Post-Fed Hangover Weighs on Markets
U.S. stocks slumped Tuesday, led by sharp losses in technology shares, as investors contended with lingering concerns over last week’s Federal Reserve meeting, the risk of a government shutdown, valuation worries, and a steep Bitcoin drop below $100,000.
The NASDAQ Composite tumbled 2.04%, marking its worst session in weeks. The S&P 500 fell 1.17%, while the Dow Jones Industrial Average declined 0.53%.
Tech heavyweights bore the brunt of the selloff. Meta Platforms dropped for the fourth consecutive day, down 16% since reporting earnings last week. Nvidia fell 3.96%, Broadcom lost 2.93%, Micron slid 7.13%, and Shopify plunged 6.93%. Oracle slipped 3.75%, ahead of its results due after the close.
Palantir Technologies sank 7.95% despite an earnings beat, as investors questioned valuation levels following its post-results rally.
Earnings Highlights
AMD (Advanced Micro Devices)
- Revenue: $9.25B vs. $8.72B est ✅
- EPS: $1.20 adj. vs. $1.16 est ✅
- Gross Margin: 52%
- Net Income: $1.24B (Adj. $1.97B vs. $1.89B est)
- Q4 Revenue Forecast: $9.6B
Strong AI and data-center demand drove a top- and bottom-line beat, with management guiding for continued growth into year-end.
Upstart Holdings (UPST)
- Revenue: $277.1M (vs. $279.8M est) ⚪
- Adj. EPS: $0.52 (vs. $0.42 est) ✅
- Adj. EBITDA: $71.2M (vs. $56.3M est) ✅
- FY25 Revenue Outlook: ~$1.04B (vs. $1.06B est) ⚠️
Q3 revenue surged 71% YoY, while originations jumped 80%. CEO Dave Girouard said Upstart’s AI platform “continues to adapt to macro signals while delivering strong credit performance.”
Pinterest (PINS)
- Revenue: $1.05B (in line)
- Adj. EPS: $0.38 (vs. $0.42 est) ⚠️
- MAU: 600M (vs. 590M est) ✅
- Adj. EBITDA: $306M (+24% YoY)
- Q4 Revenue Guide: $1.31B–$1.34B
CEO Bill Ready highlighted “record user growth” and said investments in AI are transforming Pinterest “into an AI-powered shopping assistant.”
Cava Group (CAVA)
- Revenue: $292.2M (vs. $291.5M est) ✅
- Adj. EPS: $0.12 (vs. $0.13 est) ⚪
- Same-Restaurant Sales: +1.9% (vs. +2.67% est) ⚠️
- FY25 Guide Cut: Comp sales +3–4% (prior +4–6%)
CEO Brett Schulman said new-store productivity remains strong despite macro headwinds, with average unit volumes trending above $3M.
Rivian Automotive (RIVN)
- Revenue: $1.56B (vs. $1.49B est) ✅
- Adj. Loss/Share: ($0.65) (vs. ($0.71) est) ✅
- Deliveries: 13,201 (vs. 12,972 est) ✅
- Gross Profit: $24M, up $416M YoY
- Cash: $4.44B
Rivian reaffirmed 2025 delivery guidance of 41,500–43,500 vehicles and said its R2 launch remains on track for 1H 2026. CEO RJ Scaringe said Rivian’s “vertically integrated tech and direct ownership model position us to build a category-defining brand.”
Apollo Withdraws $64-Per-Share Bid for Papa John’s; Stock Slides
Apollo Global Management has withdrawn its $64-per-share offer to acquire Papa John’s International, sending the pizza chain’s stock down 11.5% on Tuesday, according to Reuters sources.
The private-equity firm reportedly pulled the bid about a week ago amid signs of slowing consumer spending and growing weakness across the quick-service restaurant industry.
Papa John’s shares had already been trading well below the proposed offer price, suggesting investors doubted the deal’s completion. The move comes as restaurant peers such as Chipotle Mexican Grill have also seen steep share declines in recent weeks.
The decision underscores the sector’s growing vulnerability to softer discretionary demand and margin pressure as higher costs and weaker traffic hit sales.

Standard Chartered Maintains Bullish View on Global Equities Despite Valuation Risks
Standard Chartered remains positive on global equities heading into year-end, citing earnings strength and Fed easing as offsets to valuation concerns and soft U.S. jobs data.
The bank said its quantitative models — short and long term — remain “unambiguously bullish.” It expects continued support from profit growth, positive revisions, and policy easing.
Regionally, Standard Chartered stays overweight U.S. and Asia ex-Japan equities, preferring stocks over credit given “better upside potential” in the current environment. It warned, however, that volatility may persist as markets digest trade and central-bank developments.
UBS Sees Global Equity Rally Extending Despite Fed Policy Fog and Rich Valuations
UBS Group AG remains bullish on equities, saying the global bull market still has further to run even as investors fret over lofty valuations and the uncertain U.S. monetary-policy outlook amid a government shutdown.
Ulrike Hoffmann-Burchardi, global head of equities at UBS Financial Services, said persistent concern about expensive market multiples and the Federal Reserve’s unclear path “shouldn’t obscure the strength of fundamentals.”
“Despite strong gains this year, we continue to see room for the bull market to extend,” she said, urging investors to stay positioned for additional upside once policy clarity returns.
UBS analysts cited several supports:
- Corporate earnings remain above forecasts.
- Liquidity conditions are improving.
- Global risk appetite stays resilient.
The bank expects equities to grind higher into next year as the Fed edges closer to policy easing after the shutdown ends and inflation keeps cooling. While short-term volatility is likely as investors parse conflicting data, UBS said fundamentals remain in favor of risk assets.
The upbeat tone could steady market sentiment after recent swings and reinforce limited downside risk for global stocks even with yields elevated.
Rabobank: U.S. Productivity Strength Keeps Dollar Supported, But Gains Limited
Rabobank expects the U.S. dollar to remain resilient thanks to the nation’s productivity advantage, though its upside could moderate as other regions regain economic momentum.
Strategist Jane Foley said productivity gains continue to drive wealth creation and offset inflation, with technology-heavy industries sustaining U.S. competitiveness despite elevated valuations.
However, she warned the dollar’s rally may slow as global growth broadens. Japan’s emergence from deflation, Africa’s expanding resource exports, Germany’s planned fiscal stimulus, and central-bank gold buying could all reduce reliance on U.S. assets.
OpenAI Strikes $38 Billion AWS Cloud Deal to Secure Nvidia-Powered Infrastructure
OpenAI has signed a seven-year, $38 billion agreement with Amazon Web Services to lock in Nvidia-based computing power for training and deploying advanced AI systems, expanding its infrastructure beyond its Microsoft ties.
Under the deal, AWS will provide clusters of Nvidia GB200 and GB300 chips across purpose-built data centers, with full capacity expected online by end-2026. The pact allows further expansion after 2027.
The partnership is a significant boost for Amazon’s cloud division and underscores the growing capital intensity of AI development.
The deal is expected to bolster sentiment around Amazon, Nvidia, and other cloud providers, highlighting escalating competition among Big Tech firms in building next-generation AI ecosystems.
Canada Widens Deficit and Debt Forecasts as Growth Outlook Weakens
Canada’s government projected larger fiscal deficits and higher debt ratios in its latest fiscal update Tuesday, as elevated borrowing costs and slower growth weigh on public finances.
The 2025–26 deficit is now forecast at C$78.3 billion, nearly double the C$42.2 billion projected in December. The 2026–27 shortfall is seen at C$65.4 billion, up from C$31 billion, narrowing only modestly to C$63.5 billion by 2027–28.
The federal debt-to-GDP ratio is expected to rise from 42.4% in 2025–26 to 43.3% in 2027–28 before stabilizing. Despite larger deficits, gross borrowing requirements are projected to decline slightly to C$594 billion in 2026–27 from C$614 billion the prior year.
- Bond issuance: C$298B (vs. C$316B previously)
- Treasury bills: C$291B (vs. C$296B forecast in July)
- Refinancing share: ~75% of total borrowings
The budget includes C$280 billion in investments over five years targeting infrastructure, housing, defence, and competitiveness, partially offset by C$60 billion in planned savings.
Public debt charges are set to rise from C$55.6B in 2025–26 to C$66.2B by 2027–28, highlighting the impact of sustained high interest rates.
Growth forecasts were revised lower:
- 2025: 1.1% (from 1.7%)
- 2026: 1.2% (from 2.1%)
- 2027–28: ~2.0%
The Finance Ministry reaffirmed its commitment to regular green bond issuance under its sustainable financing framework.
Commodities News
Gold Rebounds After Sharp Sell-Off, But Momentum Still Weak
Gold staged a partial rebound Tuesday after tumbling more than $70 earlier in U.S. trading as a stronger dollar and weaker equities triggered a sharp flight from commodities.
Prices fell to $3,929 before recovering to around $3,966, still $35 lower on the day. The metal had dropped as much as $30 in early trading, marking one of its most volatile sessions in weeks.
Analysts said the swings reflect ongoing consolidation after gold’s steep September-October rally. “We’re skidding along the bottom of the $3,800–$4,400 range,” one trader said, noting that a stronger bounce would be needed to confirm stability.
Fundamentally, the pullback coincides with improving U.S.–China relations, speculation that the U.S. Supreme Court could curb tariffs, and expectations of a Fed pause—all reducing safe-haven demand. Even so, prices have shown resilience given recent negative headlines.
Crude Oil Settles at $60.56 as Bulls and Bears Battle for Control
Crude oil futures settled $0.45 lower at $60.56 per barrel, a decline of 0.69%, after trading between $59.94 and $61.03. The market remains rangebound as buyers and sellers battle for direction.
Technically, the commodity continues to trade below a key resistance zone between $61.45 and $61.94. On the downside, support lies between $59.64 and $60.17, levels tested repeatedly since October 10.
The 100-hour and 200-hour moving averages, near $60.60 and $60.88, are acting as short-term pivot points. Traders said the market has been consolidating between these levels since October 27, awaiting a catalyst for the next directional move.
Codelco Cuts Output Forecast as Global Copper Market Tightens
The global copper market is tightening further as production disruptions mount across major mines and new projects struggle to deliver, underscoring deep structural shortages despite record prices.
Chile’s state-owned miner Codelco — the world’s largest copper producer — posted $607 million in earnings for the first nine months of the year and trimmed its annual output guidance to 1.31–1.34 million metric tons from a prior 1.34–1.37 million.
CEO Rubén Alvarado said he remains optimistic on prices, citing chronic underproduction across the industry. Accidents at Freeport-McMoRan’s Grasberg mine and Codelco’s El Teniente operation — the latter expected to take three years to fully recover — have compounded supply stress.
Other setbacks include Ivanhoe’s Kamoa-Kakula mine facing seismic issues in Africa and the prolonged shutdown of Cobre Panamá following protests.
At the same time, grade deterioration and a lack of new discoveries are making supply growth increasingly difficult. “Underinvestment has been the story of the past decade,” analysts said.
Despite record copper prices, Codelco’s modest profits highlight why few companies are investing heavily in mining compared with high-return tech sectors — a dynamic likely to exacerbate long-term shortages.

Panama Canal Sees 2026 Trade Slowdown as U.S.–Asia LPG Shipments Surge
The Panama Canal Authority expects weaker overall trade next year as global demand slows but said liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) shipments are hitting record highs.
Administrator Ricaurte Vásquez said world trade will likely contract amid the global slowdown, but noted that U.S. LPG exports to Asia now account for over 95% of canal traffic in that category, up from 80%.
He said strong Asian demand and U.S. export growth should keep energy shipments buoyant, offsetting softer bulk and container volumes. Vásquez also mentioned rising U.S. interest in a proposed LPG pipeline to ease congestion and improve efficiency.
Spot Gold Under Pressure as China Ends VAT Rebate — ING
Spot gold prices fell after China announced the end of a value-added tax rebate on retail gold sales, effectively increasing costs for investors and consumers, according to ING analysts Ewa Manthey and Warren Patterson.
The policy removes the VAT offset previously applied to gold sold through the Shanghai Gold Exchange, covering both investment-grade and non-investment products.
“The change effectively makes gold more expensive for Chinese buyers,” ING said, warning that the move could weigh on near-term demand in the world’s largest physical gold market.
Standard Chartered Says Gold Dip Below $4,360 a Buying Opportunity, Keeps $4,500 Target
Standard Chartered is holding its 12-month gold target at $4,500 per ounce, calling the metal’s recent pullback below $4,360 a chance to buy as its key supports — weak dollar, inflation fears, and central-bank buying — stay intact.
The bank said gold remains up 49% over the past year, supported by geopolitical risk and ongoing diversification away from fiat currencies. Analysts see strong technical support between $3,945 and $4,060.
Standard Chartered added that central-bank demand and structural weakness in the dollar are likely to sustain upside momentum through 2026.
OPEC+ Signals Pause in Supply Increases Amid Expected Surplus — ING
OPEC+ said it will pause oil supply increases through the first quarter of next year after confirming a modest 137,000 b/d rise for December, according to ING commodity strategists Ewa Manthey and Warren Patterson.
“The market is expected to be in peak surplus through Q1 2026, so a pause makes sense,” they wrote. However, U.S. sanctions on Russia could disrupt flows and reduce that surplus sooner than anticipated.
Speculators boosted net-long positions in ICE Brent by 119,046 lots last week to 171,567, driven by a combination of fresh longs and short covering following the sanctions. ICE Gasoil positions also surged, with traders buying 33,930 lots amid concerns over Russian diesel exports after drone attacks on refineries.
Meanwhile, U.S. drilling continues to decline, with Baker Hughes reporting the rig count down by six to 414, even as U.S. crude output hit a record 13.79 million b/d in August, up 2.9% year-on-year.
ING said expectations of a large surplus and soft prices suggest U.S. output growth will stall in 2026, reinforcing OPEC+’s cautious stance.
China’s Metals Body Urges Curbs on New Copper Smelters — Commerzbank
China’s Nonferrous Metals Industry Association has called on Beijing to restrict new copper, zinc, and lead smelting projects, warning that record-low processing fees and mounting overcapacity threaten industry stability, Commerzbank said.
The group submitted proposals to the central government recommending strict controls on new copper capacity, noting that treatment and refining charges have plunged to historic lows due to excessive domestic competition.
If implemented, the move would represent China’s biggest metals-market intervention since the 2017 aluminum production cap, potentially tightening the global copper supply chain even as demand for energy-transition metals rises.
South Korea Plans Steel-Sector Restructure Amid Tariff Strain, Oversupply
South Korea’s government will overhaul its steel industry and step up export assistance as rising tariffs from the U.S. and EU and persistent oversupply threaten the sector’s viability.
The Trade, Industry and Energy Ministry said it will take “preemptive measures” to cut capacity in oversupplied segments while rolling out targeted financing and innovation programs to help producers withstand trade barriers.
The initiative includes production realignment, subsidies for higher-value products, and investment in low-carbon technologies. Analysts said the move signals growing concern over deteriorating profitability and shrinking global demand that have pushed the sector to the brink.
Europe News

ECB’s Rehn: Downside Risks Dominate as Uncertainty Stays High
European Central Bank policymaker Olli Rehn said uncertainty over future economic developments remains high and the balance of risks is tilted to the downside, signaling that the ECB is likely to remain cautious in the near term.
“The ECB continues to maintain a guarded stance,” Rehn said, suggesting policymakers are inclined to stay on the sidelines at least until early next year as they assess growth and inflation dynamics.
ECB’s Patsalides: Europe Showing Resilience, Needs Stronger Competitiveness
ECB policymaker Christodoulos Patsalides said the European economy is demonstrating resilience but urged governments to boost competitiveness and reduce public debt to sustain growth momentum.
Patsalides, who has previously leaned toward the hawkish camp, did not comment directly on monetary policy but emphasized that fiscal reform and productivity gains remain critical for long-term stability across the eurozone.
SNB’s Schlegel: Inflation to Edge Higher in Coming Quarters
Swiss National Bank Chairman Martin Schlegel said inflation in Switzerland is expected to rise slightly in the next few quarters, while global growth faces headwinds from U.S. tariffs.
In a presentation repeating recent remarks, Schlegel reiterated that the SNB remains focused on maintaining price stability amid weaker global trade conditions.
SNB’s Tschudin: Negative Rates Only if Necessary, FX Policy Flexible
Swiss National Bank policymaker Petra Tschudin said the SNB will only consider negative interest rates if absolutely necessary, stressing that current rates are “where they should be” to maintain inflation within the 0–2% target range.
“The key question isn’t whether the franc is correctly valued but how its movements affect inflation,” Tschudin said.
She noted that inflation forecasts — averaging 0.4% in Q4 2025 — are in line with the SNB’s objectives. FX interventions remain possible, she added, to counter excessive currency strength.
“We’re keeping rates low so inflation stays in range,” she said, adding that the bank is not seeking lower inflation and will act flexibly to preserve price stability.
UK’s Reeves: Since last year’s budget, the world has thrown more challenges our way
- Remarks by UK finance minister, Rachel Reeves
- Inflation has been too slow to come down
- Interest rates are still a constraint
- The cost of government borrowing has increased around the world
- My commitment to the fiscal rules is iron clad
- I am not satisfied, there is more to do
EU’s Šefčovič Highlights Nexperia Progress, Calls for Lasting Chip-Supply Stability
European Commission Executive Vice President Maroš Šefčovič said the EU is making headway on the Nexperia issue and remains intent on securing long-term stability in semiconductor supply without resorting to export restrictions.
Šefčovič welcomed “progress on Nexperia, which is key to restoring a secure semiconductor supply chain,” and said Brussels aims to ensure “lasting stability without export barriers.” His comments point to a cautious thaw in EU-China chip tensions and a renewed push to balance supply-chain resilience with open trade.
The statement follows Dutch government intervention in Nexperia, the China-owned chipmaker, on national-security grounds — a move that triggered Beijing’s export curbs on related products and stirred concern among European automakers and manufacturers about possible supply disruptions.
MUFG Sees Bank of England Holding Rates, December Cut Still Likely
MUFG expects the Bank of England to keep rates unchanged this week, maintaining its call for the first cut in December, according to strategist Lee Hardman.
He said one softer inflation print “isn’t enough” to shift policy now, though more evidence and fiscal signals by year-end could open the door. Hardman added that any short-term pound rally after a hold would likely fade as traders refocus on the December meeting.
Asia-Pacific & World News
Xi Reaffirms China-Russia Cooperation, Urges Expansion Into Emerging Sectors
Chinese President Xi Jinping reaffirmed his commitment to deepening strategic cooperation with Russia, saying both sides should enhance communication and broaden joint development across traditional and new industries.
Speaking after meeting Russian Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin, Xi said China and Russia should “steadily expand mutual investment” and “create new growth drivers for cooperation.”
He highlighted opportunities in artificial intelligence, the digital economy, and green development, alongside continued collaboration in energy and agriculture.
The meeting underscored Beijing and Moscow’s effort to reinforce economic ties amid global geopolitical tensions, signaling that their partnership is evolving from traditional resource trade to more high-tech and sustainable sectors.
China Offers Major Power Subsidies to Support Domestic AI Chips
China is offering substantial energy subsidies to ByteDance, Alibaba, and Tencent to offset the high electricity costs of using local AI chips from Huawei and Cambricon, according to people familiar with the policy.
Regional governments in Guizhou, Gansu, and Inner Mongolia are covering up to 50% of power bills for qualifying data centers, excluding those using Nvidia hardware banned under U.S. export controls.
The move is designed to accelerate China’s AI self-sufficiency push and mitigate the cost gap between domestic and foreign chips. Some subsidies reportedly cover an entire year of operating expenses.
Analysts say the plan highlights Beijing’s resolve to scale local semiconductor production despite performance shortfalls, likely boosting Chinese AI and chip equities.
China Begins Trial Production at World’s First Flying-Car Factory
China launched trial production at the world’s first flying-car factory in Guangzhou, marking a milestone in the country’s advanced-mobility ambitions.
The 120,000-square-meter facility will produce detachable electric aircraft modules for modular flying cars, initially targeting 5,000 units a year with capacity to double to 10,000. Once fully operational, one vehicle will roll out every 30 minutes.
The project underscores China’s drive to lead in next-generation urban transport, integrating automotive and aviation technologies to meet future mobility demand.
China, Russia Pledge Deeper Cooperation as Strategic Partnership Strengthens
China and Russia vowed to expand collaboration across trade, energy, and technology as their “comprehensive strategic partnership for a new era” reaches record levels.
At a meeting in Hangzhou, Premier Li Qiang told Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin that Beijing aims to align development strategies and enhance coordination across all sectors. Mishustin said Russia is ready to deepen joint projects in investment, logistics, and digital industries.
Both sides signed agreements on customs and satellite navigation, signaling intent to formalize long-term cooperation outside Western frameworks — a move likely to reshape Eurasian trade and security dynamics.
China’s He Lifeng Pledges to Stabilize Global Trade, Strengthen Cooperation
Chinese Vice Premier He Lifeng said Beijing will work with international partners to bolster global trade and industrial cooperation as the world economy faces new challenges.
In a Monday address, He cited rising protectionism and geopolitical strain but said China would continue promoting open markets and supply-chain stability. “We will cooperate with all parties to secure stable global industrial and trade systems,” he said.
The comments reinforce Beijing’s image as a stabilizing force amid slowing growth and underline its intent to remain a central player in international economic coordination.
PBOC to Deepen Policy Support, Expand Offshore Yuan and Cross-Border Payments
China’s central bank pledged fresh policy support and new steps to internationalize the yuan, including expanding Hong Kong’s offshore RMB market and cross-border payment channels.
A deputy governor said the People’s Bank of China will accelerate development of a “deeper, more liquid” offshore yuan market and widen the reach of the RMB Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS).
As of September, 1,176 foreign institutions held a combined 3.8 trillion yuan ($525 billion) in onshore bonds, underscoring continued international participation despite global volatility.
The measures reflect Beijing’s twin priorities: stabilizing growth and advancing the renminbi’s global role through financial integration with Hong Kong.
PBOC sets USD/ CNY central rate at 7.0885 (vs. estimate at 7.1226)
- Meanwhile PBOC dep gov says will strengthen policy support
- PBOC injects 117.5bn yuan at 1.40% via 7-day reverse repos

RBA Holds at 3.6%, Warns on Sticky Inflation, Signals Long On-Hold Period
The Reserve Bank of Australia left its cash rate at 3.6% in November, matching expectations, while cautioning that inflation remains higher than desired and the outlook uncertain.
The RBA said domestic activity is firming but underlying price pressures persist, prompting policymakers to keep a cautious stance. The central forecast sees trimmed-mean inflation peaking at 3.7% by mid-2026 before easing to 2.6% by 2027 — implying rates will stay restrictive longer than markets anticipate.
GDP growth is projected around 2% annually through 2027, with unemployment steady near 4.4%. The Bank said financial conditions are “closer to neutral” but will keep policy tight until inflation returns sustainably to target.
Overall, the tone was slightly more hawkish, signaling a slow and extended path to any future rate cuts.
RBA’s Bullock: No Discussion of Rate Cuts, Policy at ‘Right Spot’
Reserve Bank of Australia Governor Michele Bullock said policymakers did not consider cutting interest rates at their latest meeting, emphasizing a cautious stance as inflation remains above target.
“We discussed holding and the outlook for policy,” Bullock said at a post-meeting press conference. “There are mixed signals on how tight financial conditions are. We still have a little bit of tightness that will take some heat out of the economy to bring inflation back down.”
She added that while more cuts are possible, the board believes previous easing is still working through the economy. “It’s possible that there are no more rate cuts, but also possible that there will be some. We didn’t go up as high, so we don’t have to come down as far,” she said, clarifying that a rate hike was not discussed.
Bullock stressed that the RBA is targeting a 2.5% inflation rate, saying “just below 3% is not good enough.” The board has no policy bias, will go meeting by meeting, and is “watching things carefully.”
“We think we are close to neutral,” she said, adding that while mortgage holders want more relief, it’s “also important to keep inflation under control — that’s what really affects living standards.”
Japan’s Takaichi: Inflation Yet to Meet BOJ’s 2% Target Sustainably
Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi said inflation has yet to reach the Bank of Japan’s price target on a sustained basis and called on the central bank to continue appropriate monetary policy coordination with the government.
“Japan is still halfway through achieving a stable 2% price target,” she said, urging close cooperation with the BOJ.
Takaichi credited Abenomics with boosting GDP and job creation, and said the government will “strategically deploy fiscal spending to raise household income and consumer sentiment.”
Her remarks suggest continuity in Japan’s pro-growth stance and support for maintaining policy coordination as the economy seeks durable inflation momentum.
Japan Finance Minister Katayama Flags “One-Sided” Rapid Yen Moves
Japan’s Finance Minister Katayama said authorities are watching currency markets “with a high sense of urgency,” describing recent yen movements as “one-sided and rapid.” The remarks suggest Tokyo may be preparing to intervene if volatility intensifies.
Japan Manufacturing PMI Slumps to 48.2, Weakest in 19 Months
Japan’s manufacturing activity contracted at the fastest pace in more than a year, with the S&P Global PMI falling to 48.2 in October from 48.5, below the flash reading of 49.3.
The downturn reflected steep drops in new and export orders, particularly in autos and semiconductors, and rising input costs. Output prices climbed as firms passed on higher labor and material expenses.
Despite the gloom, business sentiment improved modestly on expectations of AI adoption, new product launches, and eventual global trade recovery. Still, the weak PMI underscores Japan’s industrial fragility as the Bank of Japan faces pressure to normalize policy amid stubborn inflation.
Japan’s Takaichi Vows to Lift Revenue via Growth, Not Tax Hikes
Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi reaffirmed Japan’s commitment to raising fiscal revenue through economic expansion rather than tax increases, emphasizing supply-side investment and productivity gains.
Takaichi said her government will boost infrastructure, strengthen industrial capacity, and compile a new growth strategy by next summer. She framed the approach as pro-growth and fiscally disciplined — aimed at stimulating demand while avoiding extra burdens on households or companies.
Her remarks suggest policy continuity and may support equity sentiment while weighing on the yen.
South Korea Inflation Accelerates to 2.4%, Fastest Since Mid-2024
South Korea’s inflation rate quickened to 2.4% in October from 2.0% in September, marking its fastest annual rise since July 2024 and outpacing forecasts for 2.1%, according to government data released Tuesday.
Prices rose 0.3% on the month, versus expectations for no change, as higher utility, service, and fresh-food costs drove the increase. Core CPI — excluding food and energy — climbed 2.2% year-on-year, up from 2.0%.
Officials said the acceleration reflects broad-based pressures as domestic demand firms and energy costs stabilize at elevated levels. The result complicates expectations for Bank of Korea rate cuts early next year, suggesting policy will stay restrictive for longer.
October CPI details:
- +0.3% m/m (est. 0.0%, prior +0.5%)
- +2.4% y/y (est. +2.1%, prior +2.1%)
- Core CPI +2.2% y/y (prior +2.0%)
Crypto Market Pulse
Bitcoin Breaks Below $100,000 for First Time Since June
Bitcoin slipped under the $100,000 mark for the first time since June 23, extending a month-long downtrend that has erased more than 20% from its October peak.
The world’s largest cryptocurrency fell to an intraday low of $99,939, its weakest since $99,705 on June 23. From the October 6 high of $126,272, Bitcoin has dropped 20.89% over 29 trading days, reflecting persistent risk aversion and profit-taking.
On technical charts, traders are eyeing support near the June 22 low of $98,240, followed by the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement of the August-to-October rally at $96,975.
Analysts say the loss of the six-figure handle could invite further downside pressure as momentum shifts away from the crypto complex amid falling ETF inflows and broad risk-off sentiment.
XRP Extends Sell-Off as Ripple Expands Into Digital-Asset Custody
XRP slipped toward $2.18 support on Tuesday, down to around $2.26 intraday, as risk aversion deepened across cryptocurrencies. Liquidations in the digital-asset market totaled $1.33 billion over the past 24 hours, according to CoinGlass data.
Meanwhile, Ripple Labs announced the acquisition of Palisade, a digital-asset wallet and custody provider, to expand institutional infrastructure for fintechs, corporates, and crypto-native firms.
Ripple said the deal will integrate Palisade’s “wallet-as-a-service” technology into Ripple Payments, enabling subscription-based payments and faster transaction settlement. “The combination of Ripple’s bank-grade vault and Palisade’s lightweight wallet makes Ripple Custody an end-to-end provider for institutional needs,” President Monica Long said.
Ripple has spent roughly $4 billion this year on ecosystem investments, including the acquisitions of Hidden Road (now Ripple Prime) and GTreasury.
Despite the expansion, XRP remains under pressure, down nearly 38% from its mid-July high of $3.66, as traders shift to short positions. The OI-weighted funding rate fell to –0.0019% from 0.0085%, signaling a sharp sentiment reversal.
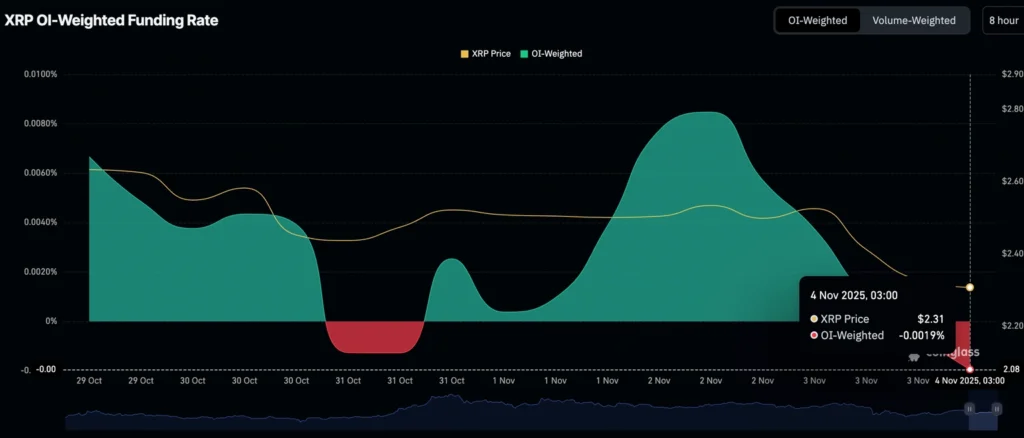
Tron Risks Breaking Key Support as User Activity, Demand Slide
Tron (TRX) traded around $0.2800 Tuesday, under pressure after a 5.6% decline Monday, as both on-chain and derivatives data point to weakening demand.
The token is testing a year-long support trendline, with DeFiLlama data showing Total Value Locked (TVL) on the Tron network down 6.57% in the past 24 hours to $4.97 billion. The drop signals that users are withdrawing assets, reducing liquidity and engagement.
In derivatives markets, CoinGlass reported TRX futures open interest fell 1.68% to $290.5 million, suggesting traders are cutting leverage or closing positions amid deteriorating sentiment.
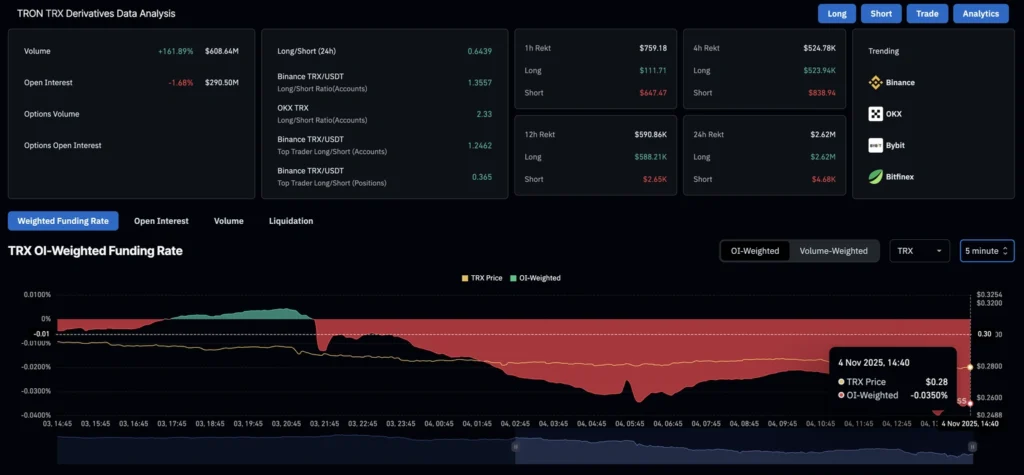
Analysts warn that a break below trend support could trigger further selling as participation wanes across the Tron ecosystem.

Crypto Market Slides as ETF Outflows Deepen; Bitcoin, Ether, XRP Drop
Cryptocurrencies fell again Tuesday as retail and institutional investors continued to pare exposure, with Bitcoin (BTC) dropping toward its October low of $102,000, Ethereum (ETH) sliding below $3,500, and XRP hovering near $2.26.
The broad retreat follows accelerating ETF outflows. U.S.-listed Bitcoin spot ETFs saw $187 million withdrawn Monday, marking the fourth straight day of redemptions and bringing total inflows to $61 billion and net assets to $143.5 billion.
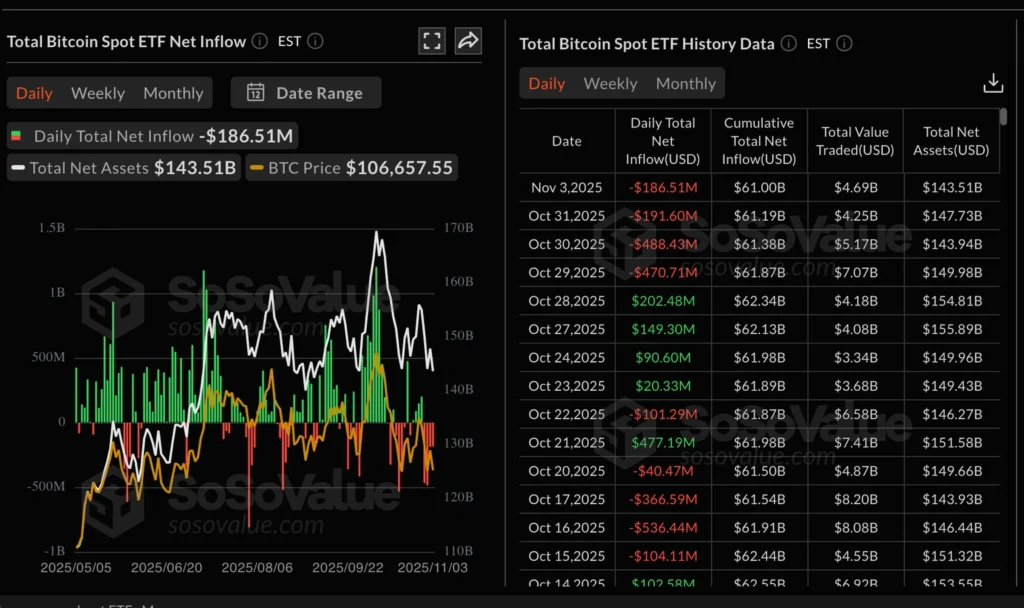
Ethereum ETFs also posted $136 million in outflows, led by BlackRock’s ETHA (–$82 million) and Fidelity’s FETH (–$25 million). Combined ETH ETF inflows stand at $14.23 billion with about $24 billion in assets.
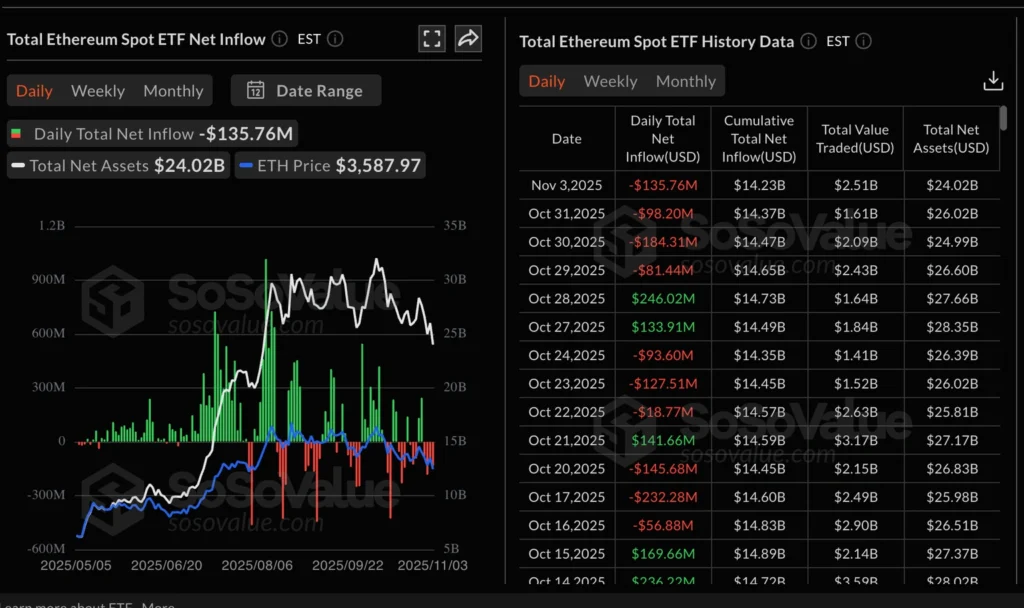
Analysts say the persistent withdrawals reflect fading confidence in digital-asset funds and could amplify near-term downside risk across major tokens as both institutional and retail traders exit.
Sui Falls 15% as Staking Balances Shrink, Sentiment Weakens
Sui (SUI) extended losses Tuesday, testing $2.00 after three straight days of declines. The Layer-1 token has fallen 14% since early November as risk-off sentiment persists across crypto markets.
DeFi data show Sui’s Total Value Locked (TVL) fell 4.76% in the past 24 hours to $1.6 billion, reflecting investors pulling capital from staking and DeFi protocols.
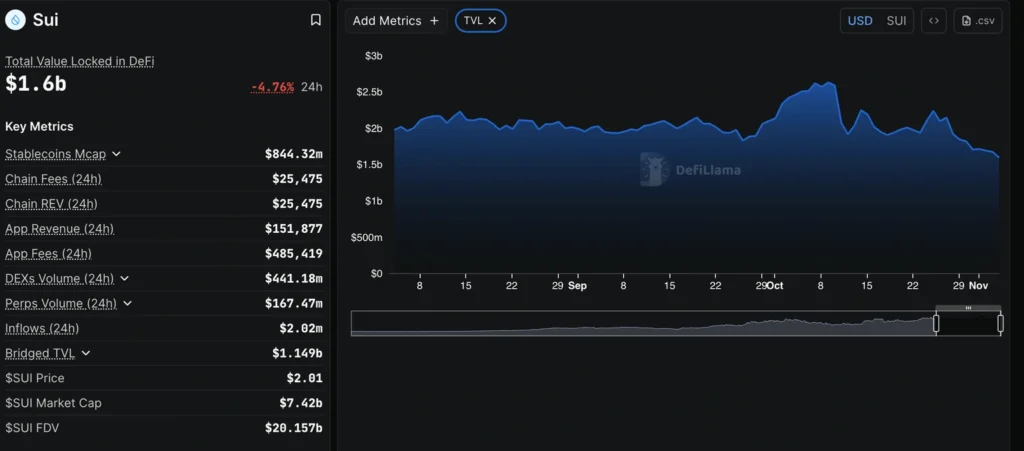
Analysts said the trend points to waning confidence in Sui’s growth outlook. “When holders withdraw from smart contracts, it’s a sign sentiment has turned,” one trader noted.
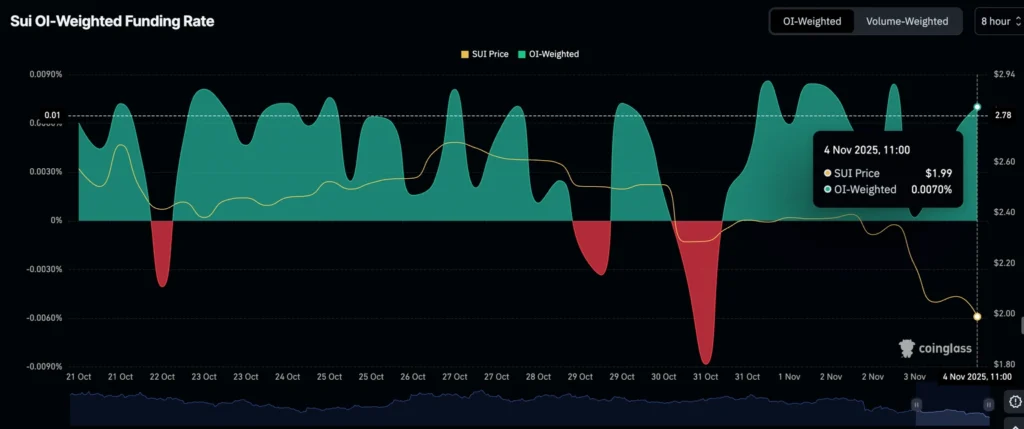
Still, some investors are positioning for a rebound: the open-interest-weighted funding rate rose to 0.0070% from 0.0002% Monday, suggesting traders are cautiously re-entering long positions as the token holds above key support.
Ether Falls Below $3,600 After $100 Million DeFi Hack Hits Confidence
Ether extended losses on Monday, sinking below $3,600 after hackers stole more than $100 million from the decentralized-finance platform Balancer, adding to selling pressure already fueled by macro uncertainty and a cautious Federal Reserve.
The drop — as steep as 9% intraday — leaves the world’s second-largest cryptocurrency down about 25% from its August 22 peak of $4,885. Analysts said the breach reignited concerns over security and liquidity just as risk appetite weakens.
Crypto-linked equities, including exchanges and miners, also traded lower in sympathy. Market strategists warned Ether’s break of key technical support could prompt further downside amid waning confidence.
The Balancer exploit compounds a series of security setbacks in the DeFi sector, highlighting vulnerabilities that continue to weigh on sentiment as global liquidity tightens.
Ether (ETH) powers the Ethereum blockchain, which underpins most decentralized-finance and NFT applications.

The Day’s Takeaway
North America
U.S. equities fell across the board as technology names led a rout: the NASDAQ plunged 2.04%, the S&P 500 lost 1.17% and the Dow slid 0.53%. Fresh headwinds included the lingering fallout from the Fed meeting, the U.S. government shutdown, valuation concerns and crypto weakness after Bitcoin dipped below $100,000.
Mega-cap techs were notable drags — Meta extended losses for a fourth day (roughly -16% since its earnings), Nvidia -3.96%, Broadcom -2.93%, Micron -7.13%, Shopify -6.93% and Oracle slipped ahead of after-hours results. Palantir dropped despite an earnings beat, as investors questioned stretched multiples.
Earnings paint a mixed picture: AMD beat on revenue ($9.25B) and adjusted EPS ($1.20), citing AI and data-center strength and guiding higher for Q4; Upstart delivered robust margins and growth but slightly missed revenue consensus; Pinterest posted user gains but a small EPS miss; Cava trimmed some guidance despite top-line growth; Rivian beat delivery and revenue expectations while narrowing losses and holding a sizable cash buffer.
In Canada, Ottawa widened fiscal deficits sharply — the 2025/26 shortfall is now C$78.3bn (vs C$42.2bn prior) and debt-to-GDP is forecast rising toward ~43%, even as gross borrowing needs edge down. The update dampens sovereign fiscal space amid elevated debt-servicing costs.
Commodities
Gold saw extreme intraday swings — plunging more than $70 to a low near $3,929 before recovering to about $3,966, reflecting dollar strength and equity weakness but still signaling consolidation after September–October gains. Standard Chartered maintained a $4,500 12-month target, calling dips buying opportunities given central-bank demand and structural dollar dynamics.
Crude oil settled around $60.56/bbl, trading in a tight range between roughly $59.9–$61.0 as market participants balanced OPEC+’s modest December increment (137k b/d) and the group’s decision to pause additional increases into Q1 2026 against sanctions-related supply risk. U.S. rig counts slipped, even as U.S. crude output remains near record levels.
Base metals tightened: Codelco trimmed 2025 copper guidance to 1.31–1.34mt amid mine outages and accidents, underscoring underinvestment and supply risk even with record prices. China’s metals body urged curbs on new copper, zinc and lead smelters amid collapsing processing fees — a move that could reframe global capacity dynamics. Separately, China ending a retail gold VAT rebate pressured physical demand.
Europe
European policymakers struck a cautious tone. ECB official Olli Rehn warned that downside risks remain large and uncertainty is high, while Christodoulos Patsalides urged competitiveness and debt reduction. Switzerland’s SNB signalled slightly higher near-term inflation with flexible FX tools and negative rates explicitly only as a last resort. The EU’s Šefčovič reported progress on the Nexperia case and sought chip-supply stability without resorting to export barriers. MUFG expects the BoE to hold this week with a December cut still the base case.
Asia
Japan’s manufacturing PMI slid to 48.2, the weakest in 19 months, driven by weaker autos and semiconductors and softer new/export orders. South Korea’s CPI accelerated to 2.4% y/y in October (0.3% m/m) — the fastest since mid-2024 — complicating the Bank of Korea’s easing path; Seoul also announced steel-sector restructuring and export support amid tariffs and oversupply. China and Russia pledged deeper all-round cooperation; Beijing’s PBOC pledged policy support and steps to deepen the offshore yuan and CIPS expansion. China also rolled out hefty power subsidies for domestic AI-chip adoption, and trial production began at a large flying-car factory in Guangzhou.
Rest of World
Australia’s RBA held its cash rate at 3.6%, warning that inflation will remain elevated for longer and signalling a slow, meeting-by-meeting path to easing. The Panama Canal flagged a likely 2026 trade slowdown but record U.S.–Asia LPG transits, highlighting diverging traffic drivers.
Crypto
Risk aversion intensified: Bitcoin slipped under $100,000 to $99,939, down ~21% from its Oct 6 peak. Ether fell below $3,600 after a $100m Balancer DeFi hack, compounding selling. XRP slid toward support near $2.18 while Ripple acquired custody provider Palisade to expand institutional offerings. Tron and Sui both showed weakening TVL and open interest metrics, signalling declining user activity. ETF outflows accelerated — US spot BTC ETFs posted notable redemptions — amplifying downside risks across tokens.