North America News
Dow and S&P Close at Records, Nasdaq Eases After Prior High
U.S. equities ended Friday with mixed results as the Dow Jones Industrial Average and S&P 500 closed at fresh record highs, while the Nasdaq Composite slipped after setting its own peak a day earlier.
Friday closes:
- Dow Jones: 46,758.28 (+238.56, +0.51%)
- S&P 500: 6,715.79 (+0.44, +0.01%)
- Nasdaq: 22,780.51 (-63.54, -0.28%)
- Russell 2000: 2,476.17 (+17.69, +0.72%)
Weekly gains:
- Dow: +1.10%
- S&P 500: +1.09%
- Nasdaq: +1.32%
- Russell 2000: +1.72%
Healthcare led the advance with its best week since June 2022 (+6.82%), followed by utilities (+2.39%) and information technology (+2.25%). On the downside, energy (-3.34%), communication services (-2.10%), and consumer discretionary (-0.81%) lagged.
ISM US Services PMI Falls to 50.0 in September
The Institute for Supply Management’s services PMI showed the U.S. services sector stalled in September, with a headline reading of 50.0 versus expectations of 51.7 and a prior 52.0.
Breakdown of the report:
- Business activity: 49.9 (expected 51.8, prior 52.0)
- Prices paid: 69.4 (vs. 69.2 in August)
- Employment: 47.2 (up from 46.5, still in contraction for the fourth straight month)
- New orders: 50.4 (vs. 56.0 in August)
- Supplier deliveries: 52.6 (vs. 50.3 prior)
- Inventories: 47.8 (vs. 53.2 prior)
- Backlog of orders: 47.3 (vs. 40.4 prior)
- Exports: 46.5 (vs. 47.3 prior)
- Imports: 49.2 (vs. 54.6 prior)
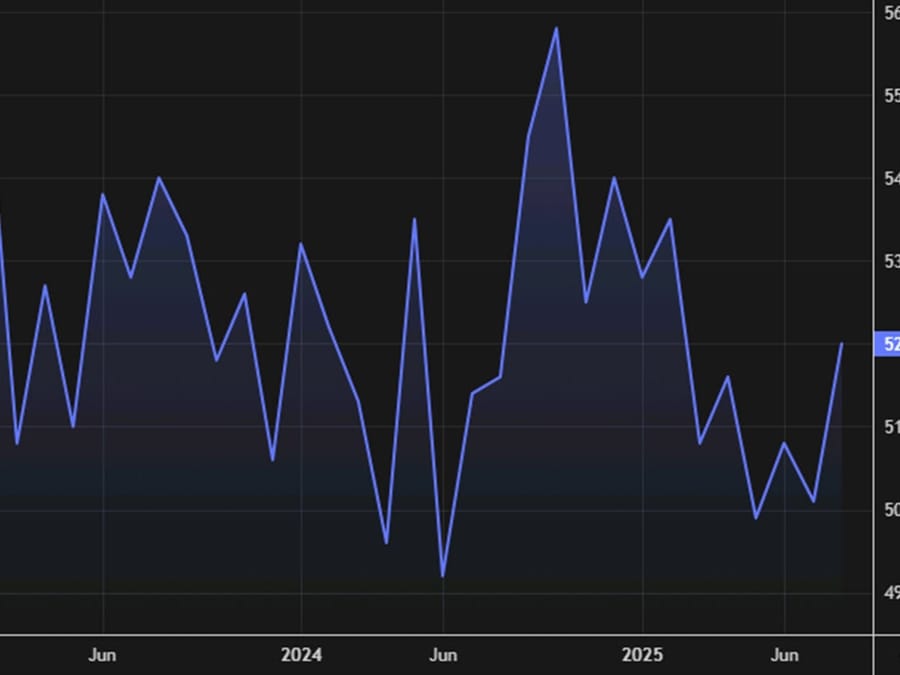
The data highlights weakness in demand and hiring, even as cost pressures remain elevated.
Comments in the report:
- “We are beginning to see the impact of the tariffs impact our business, particularly for food products from India, China, and Southeast Asia, coffee from South America, and apparel and electronics from Asia. Our year-over-year cost increases are getting progressively greater.” [Accommodation & Food Services]
- “New residential construction continues to struggle in a tough market. Housing values remain high, and tariffs are beginning to be passed through on materials that are metal based. The pace of housing starts has been stagnant to slightly declining, as we head out of the summer building season.” [Construction]
- “Pharmacy costs continue to rise, and medical devices are being held at bay mainly due to contracts and continued negotiations where we have two to three sources for a given product.” [Health Care & Social Assistance]
- “Demand for artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud infrastructure remains very strong. Our primary focus this month was on increasing production throughput to begin clearing the significant order backlog built up over the summer. While new order intake has stabilized at a high level, the overall business outlook remains positive. We are still facing significant supply chain challenges, especially for advanced semiconductors and power components, with lead times remaining extended. Price pressures are still present but have not worsened compared to the previous month.” [Information]
- “Client demand in professional services remains steady, though decision-making timelines are lengthening due to continued economic uncertainty and interest-rate concerns. We are also seeing modest upward pressure on labor costs, which impacts both our internal resourcing and supplier pricing.” [Professional, Scientific & Technical Services]
- “Growing apprehension regarding state efforts to reduce or eliminate property taxes that are a major revenue source for local governments. And continuing concern about future economic conditions, inflation, tariffs and their impact on increased prices.” [Public Administration]
- “The overall housing market remains stagnant, which has forced our company to be hyper-vigilant about costs. However, we are growing and increasing our market share despite the headwinds. Tariffs continue to inject an unnecessary level of uncertainty across the broader economy, and costs are now beginning to increase with the full effect of the tariffs now coming into play.” [Real Estate, Rental & Leasing]
- “Costs overall have stabilized, and we’ve not seen any interruptions in sourcing or shipments.” [Retail Trade]
- “We’ve had more tariff charges last month than in previous months.” [Utilities]
- “Business conditions continue to soften, even in markets that have historically been more resilient. Demand is simply weak.” [Wholesale Trade]
US September Final Services PMI Holds at 54.2
The final S&P Global Services PMI for the United States came in at 54.2 in September, above the preliminary 53.9 but slightly lower than August’s 54.5. The Composite PMI was confirmed at 53.9, up from a flash estimate of 53.6.
The data shows continued expansion, though at a softer pace. Demand and activity growth slowed slightly, while capacity constraints persisted. Backlogs of work increased for the seventh consecutive month, underscoring ongoing pressure within the sector.
Despite this, many service providers were hesitant to boost hiring, signaling caution as economic momentum moderates.
Chris Williamson, Chief Business Economist at S&P Global Market Intelligence
“Service sector growth softened slightly in September but remained strong enough to round off an impressive performance over the third quarter a whole. Combined with sustained growth in the manufacturing sector, the expansion of service sector activity is indicative of robust third quarter annualized GDP growth of around 2.5%.
“Growth is being fueled principally by rising financial services and tech sector activity, though we are also seeing more signs of improving demand for consumer-facing services such as leisure and recreation, likely linked in part to lower interest rates. Lower borrowing costs have also fed through to a broad- based improvement in business optimism about the outlook for the next 12 months.
“Disappointingly, the improvement in business optimism failed to spur more jobs growth, with hiring almost stalling in a sign of further labor market malaise as companies often focused on running more efficiently amid uncertain trading conditions.
“A further ongoing source of concern from the surveys are heightened cost pressures which survey respondents have attributed to tariffs. Input costs rose sharply again in September as import levies were seen to have again fed through from goods to services. However, rates charged for services rose at the slowest rate for five months in a welcome sign that some of these tariff price pressures in supply chains are starting to moderate.”

Fed’s Jefferson, Logan Highlight Inflation and Labor Risks
Federal Reserve officials offered mixed but cautious views on policy Friday.
Vice Chair Philip Jefferson:
- Said recent rate cuts have brought policy closer to neutral
- Pointed to declining immigration as a key reason unemployment has not risen more sharply
- Noted multiple data series now indicate labor market softening
Cleveland Fed President Lorie Logan:
- Argued policy is likely only modestly restrictive
- Warned that tariffs could have longer-lasting effects than expected
- Highlighted persistent upside risks in goods prices and elevated non-housing services inflation
Palantir Shares Slide on Leaked Memo Highlighting Security Flaws
Palantir shares dropped 4.5% after a leaked U.S. Army memo revealed critical security concerns in the company’s battlefield communications platform. The Reuters report detailed a September memo from the Army’s chief technology officer describing major risks with the NGC2 system, which integrates soldiers, sensors, vehicles, and command operations.
The memo warned: “We cannot control who sees what, we cannot see what users are doing, and we cannot verify that the software itself is secure.” It labeled the prototype as “very high risk,” cautioning that adversaries could potentially gain undetected access.
The news raised concerns about Palantir’s ability to deliver secure defense technology, weighing heavily on its stock.
Fed’s Williams: Change and Uncertainty Will Define the Economic Landscape
New York Fed President John Williams stressed that uncertainty and structural shifts in the economy will remain constants for the foreseeable future. Speaking without offering specific guidance on the monetary policy path, Williams underlined that transparency and communication are essential tools for central banks.
“Policy works better when the public understands it,” Williams said, adding that what was once seen as “unconventional” monetary policy has now become part of the standard toolkit. He argued that effective policy needs to account for a constantly evolving economic environment.
Williams emphasized that anchoring inflation expectations is central to robust monetary policy, which requires flexibility and adaptability as the economy shifts over time.
Fed’s Goolsbee: Dual Deterioration Raises Risks for the Economy
Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee warned that economic conditions are showing strain on both sides of the central bank’s mandate, pointing to rising inflationary pressures in services alongside signs of a softer outlook.
In an interview with CNBC, Goolsbee said he remains cautious about cutting rates too aggressively. “I’m wary about front-loading too many rate cuts,” he remarked, while noting that higher services inflation is a particular concern and appears unrelated to tariffs.
On the labor side, Goolsbee argued that available data still shows a relatively stable jobs market. However, he warned that the absence of official government statistics creates risks: “The longer we go without statistics, the more blind we’re going to be.” He added that while private-sector job data exists, there are fewer alternative data sources available for inflation.
Fed’s Miran: Significant Disinflation Ahead in Services Sector
Federal Reserve Governor Adriana Miran expressed confidence that services inflation will see a substantial slowdown, pointing to structural changes in the economy. Speaking on Bloomberg TV, she argued that the neutral interest rate has shifted lower and now sits at the bottom of the Fed’s estimate range.
Miran criticized the use of backward-looking data for policy decisions, saying forward-looking indicators provide a more accurate guide. She highlighted the cost of housing as a central factor in inflation dynamics, stressing that regulatory barriers have been key drivers of price pressures.
“When you remove regulations, it creates a positive output gap,” Miran explained, suggesting that loosening supply-side constraints could further ease inflation.
Bank of America Joins Consensus on October Fed Cut
Bank of America now expects the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates in October, aligning with growing market expectations. Futures markets are already pricing in a 95% probability of an October cut, with an 85% chance of cuts in both October and December.
Fed funds pricing has steadily shifted back toward dovish expectations, reversing the more hawkish stance seen earlier in September. Traders are now pricing in 105 basis points of easing over the next year, up from 94 basis points previously.
The shift is viewed as dollar-negative but supportive for U.S. equities, as investors increasingly embrace the likelihood of a sustained easing cycle.
White House Pushes Equity-for-Relief Deals Across Key Industries
President Trump is orchestrating a wide-ranging campaign to secure economic deals across as many as 30 strategic industries ahead of the 2026 midterms.
The administration is using tariff relief, regulatory concessions, and even government equity stakes to pressure companies into agreements that Trump can announce personally. Pharmaceutical firms have been a particular target:
- Eli Lilly was pressed to increase insulin production.
- Pfizer agreed to lower drug prices in exchange for tariff relief.
- AstraZeneca was urged to consider moving its U.S. headquarters.
But the effort extends beyond pharma. Critical industries like AI, semiconductors, mining, energy, shipbuilding, and batteries are all in play.
Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick is acting as the White House’s chief negotiator, overseeing equity stakes in firms like Intel and U.S. Steel. Meanwhile, J.P. Morgan reports over 100 corporate inquiries since the MP Materials deal in July.
To finance the initiative, the administration is seeking to expand the International Development Finance Corporation’s authority to $250 billion and launch a new U.S. Investment Accelerator.
Supporters argue the plan will strengthen supply chains and reduce reliance on China. Critics say it represents a break from free-market principles, turning government into a corporate power broker.
Canada’s Carney Heads to Washington for White House Talks
Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney will make a working visit to Washington, D.C. on October 7 to meet with U.S. President Donald Trump. The trip comes as Canada continues to roll back counter-tariffs in hopes of securing a broader trade deal.
Deputy Prime Minister Dominic LeBlanc has struck a more optimistic tone in recent weeks, but he admitted, “Time will tell us if my optimism is misplaced.”
Typically, such visits by heads of government are meant to finalize agreements, but the official statement from Ottawa suggests the focus will be on broader priorities. The two sides are preparing for the first joint review of CUSMA, and the agenda will center on new economic and security arrangements.
So far, there are no signs of a breakthrough, making it unlikely that Carney’s visit will yield immediate trade concessions.
Commodities News
Gold Rises Toward Record as Shutdown Drives Haven Flows
Gold prices climbed for a seventh straight week, buoyed by safe-haven demand amid a U.S. government shutdown and dovish Fed commentary.
- Friday move: +0.70%, last at $3,882, after hitting a low of $3,838
- Target: Traders eye a retest of the all-time high at $3,896
Economic data offered mixed signals: ISM services PMI stalled at 50, while S&P Global’s survey showed expansion. Missing government data—including jobless claims and nonfarm payrolls—kept markets leaning on Fed guidance.
Fed Governor Stephen Miran struck a dovish tone, calling for forward-looking policy despite the lack of fresh data. Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee warned against pre-committing to rate cuts, stressing data dependence.
Political uncertainty added to demand, with Senate gridlock keeping the shutdown unresolved. Reports also noted that China is pressing Washington to roll back security restrictions in exchange for a potential investment package.
Oil Settles Higher But Logs Steepest Weekly Drop Since June
Crude oil futures rose on Friday, though they still posted their sharpest weekly decline in over three months.
- Friday settlement: $60.88 (+$0.40, +0.66%)
- Weekly change: -$4.31 (-6.61%), worst since June 23
Markets are looking ahead to the OPEC+ decision on production levels for November. Estimates range from a modest ~140,000 bpd increase (Goldman Sachs) to 274,000–411,000 bpd, as the group continues to roll back prior cuts. Saudi Arabia favors a larger hike to regain market share, while Russia remains cautious.
Technically, WTI closed below a key swing zone between $61.45–$61.94, leaving sellers in control unless prices reclaim that range.
Baker Hughes Rig Count Flat in U.S. and Canada
The Baker Hughes rig count held steady this week in both the U.S. and Canada.
United States:
- Total rigs: 549 (unchanged)
- Oil: 422 (-2)
- Gas: 118 (+1)
- Miscellaneous: 9 (+1)
- Down 36 rigs from a year ago
- Offshore rigs: 15 (+1 on week, -3 y/y)
Canada:
- Total rigs: 190 (unchanged)
- Oil: 129 (unchanged)
- Gas: 60 (unchanged)
- Miscellaneous: 1 (unchanged)
- Down 33 rigs from a year ago

Silver Holds $47, Eyes Push Toward $50
Silver traded around $47.10 per ounce in Asian trading Friday, holding near Thursday’s 14-year peak of $48.05. Technicals show the metal moving higher within an ascending channel, keeping a bullish tone intact.
- Immediate support: $47.00 (psychological level)
- Next support: 9-day EMA at $46.02, then channel support near $43.70
- Key resistance: $48.70 at channel top, then $50.00 psychological level
The 14-day RSI remains above 70, flagging overbought conditions and potential for short-term corrections. However, staying above the 9-day EMA reinforces near-term momentum. A break above $48.70 would strengthen the uptrend and open the door toward $50.
Saudi Arabia Pushes for Bigger OPEC+ Output Increase
Ahead of this weekend’s OPEC+ meeting, Saudi Arabia is advocating for a larger increase in production, according to Bloomberg. Russia, however, is pressing for a more modest boost.
Moscow favors a 137,000 barrels per day (bpd) rise, in line with September’s adjustment. By contrast, Saudi Arabia has floated options ranging from 274,000 to 548,000 bpd.
Higher-end increases would effectively unwind the group’s voluntary cuts by the end of the year. However, such a move would leave OPEC+ with a claimed spare capacity of only 2 million bpd—figures many analysts believe are overly optimistic and unlikely to be tapped quickly.
Alberta Pledges $14M to Revive West Coast Pipeline Proposal
Alberta Premier Danielle Smith has committed $14 million in funding to restart efforts for a pipeline project that would connect Alberta’s oil sands to Asia through Prince Rupert, British Columbia.
Smith described the project as a “moral imperative” but stressed that taxpayers would not cover construction costs. The proposal mirrors the scrapped Northern Gateway pipeline and will require the federal government to repeal its tanker ban on northern B.C. waters.
Smith emphasized Indigenous participation, citing support from some Alberta First Nations leaders. However, opposition remains strong among Coastal First Nations groups.
B.C. Premier David Eby dismissed the move as political theatre, noting the lack of private-sector backing. Alberta plans to submit the project to Ottawa’s Major Projects Office in spring 2026, supported by an advisory group including Enbridge and Trans Mountain, though no construction firm or route has been secured.
Oil Market Braces for More Volatility as OPEC+, China, and Conflicts Collide
Global oil markets remain on unstable ground as multiple forces pull prices in conflicting directions.
- OPEC+ Supply Discipline: Of the 2.2 million barrels per day (bpd) in voluntary production cuts scheduled to ease, only part has actually reached markets. Around 500,000 bpd has stayed off the market, creating a bullish supply effect. Future quota increases may not matter until producers significantly boost real output.
- China’s Buying Behavior: China has stockpiled an estimated 500,000 bpd through 2025, stabilizing Brent in the $65–70 range. But imports are price-sensitive; September shipments dropped to their lowest since February after a summer price spike.
- Geopolitics: Conflicts in the Middle East, Ukrainian strikes on Russian refineries, and ongoing U.S. trade disputes continue to inject unpredictability into supply and refining margins.
The combination makes forecasting nearly impossible. Analysts warn that volatility risks are elevated as these three drivers interact in unpredictable ways.
Goldman Sachs Keeps U.S. Gas Forecasts Unchanged, Flags Medium-Term Tightness
Goldman Sachs has reaffirmed its natural gas price outlook, leaving Henry Hub forecasts steady at $4.00 per million British thermal units (mmBtu) for late 2025 and $4.60 for 2026.
The bank said short-term pricing remains largely tied to seasonal demand and storage levels, but attention will increasingly shift to supply-side constraints in the coming years. In particular, rising U.S. liquefied natural gas (LNG) exports, stronger power demand, and slowing production growth are expected to create a tighter balance.
Goldman emphasized that structural demand growth, especially from LNG and power generation, will put upward pressure on prices despite current stability. Storage remains comfortable ahead of winter, easing near-term risks, but forward markets are already looking toward 2026 for signs of a supply squeeze.
Europe News
European Stocks End Week Higher Despite DAX Dip
European markets closed mostly higher on Friday, capping a strong week of gains. The exception was Germany’s DAX, which slipped 0.18% on the day but still posted a solid weekly advance.
Friday closes:
- Euro Stoxx 50: 5,656.90 (+1.60, +0.03%)
- Germany DAX (DEU40): 24,378.81 (-43.76, -0.18%)
- France CAC 40: 8,081.55 (+24.91, +0.31%)
- UK FTSE 100: 9,491.24 (+63.50, +0.67%)
- Spain IBEX 35: 15,585.10 (+88.90, +0.57%)
- Italy FTSE MIB: 43,258.10 (+179.98, +0.42%)
Weekly performance:
- Euro Stoxx 50: +2.79%
- Germany DAX: +2.69%
- France CAC 40: +2.68%
- UK FTSE 100: +2.22%
- Spain IBEX 35: +1.53%
- Italy FTSE MIB: +1.43%
The UK’s FTSE 100 ended at a fresh record high, while Spain’s IBEX closed at its strongest level since 2007.
Eurozone Services PMI Strengthens in September
The Eurozone’s services sector provided a lift at the end of Q3, with the final HCOB Services PMI at 51.3, nearly unchanged from the preliminary 51.4.
The Composite PMI stood at 51.2, matching the flash estimate. HCOB said the uptick in new business could translate into 0.4% quarterly growth, giving the ECB confidence in its current policy approach.
HCOB notes that:
“Things are running a little bit more smoothly in the service sector. After almost stagnating in August, business activity picked up more strongly in September. This recovery is practically broad-based geographically, with moderately robust growth observed in Germany, Italy, and Spain. The situation is different in France, where the change of government and uncertainty about whether the new prime minister will be able to hold on to power has had a negative impact on service providers. Business activity declined noticeably here.
“The increase in new business suggests that the sector is likely to grow again next month. However, new orders have not yet been sufficient to increase backlogs. Nevertheless, service providers are taking a more positive view of the environment, as illustrated by the rise in the index measuring firms’ future prospects.
“The service prices data, which is under particular scrutiny by the eurozone’s monetary authorities, are likely to confirm the stance of those ECB members who do not want further interest rate cuts. Although both cost and sales price inflation rates are slightly above the long-term average, they declined in September.
“The composite PMI has been in expansionary territory for the entire third quarter, so it can be assumed that GDP has grown in that quarter. Our nowcast, which takes the PMI into account alongside other indicators, calculates a growth rate of 0.4 percent compared to the previous quarter.”
Eurozone Producer Prices Decline in August
Eurostat data showed Eurozone producer prices fell 0.3% in August, steeper than the 0.1% decline forecast. The prior month saw a 0.4% increase.
The drop was driven mainly by a 1.3% fall in energy prices. Stripping out energy, price movements were modest: capital goods (+0.1%) and non-durable consumer goods (+0.1%) edged up, while intermediate (-0.1%) and durable consumer goods (-0.1%) slipped.

Germany’s Services PMI Revised Lower, Still Expanding
Germany’s services sector remained in expansion in September, though growth was weaker than first reported. The final HCOB Services PMI came in at 51.5, down from a preliminary 52.5.
The Composite PMI was also revised lower to 52.0, compared to a preliminary 52.4. New work inflows fell for a second straight month, highlighting fragile demand.
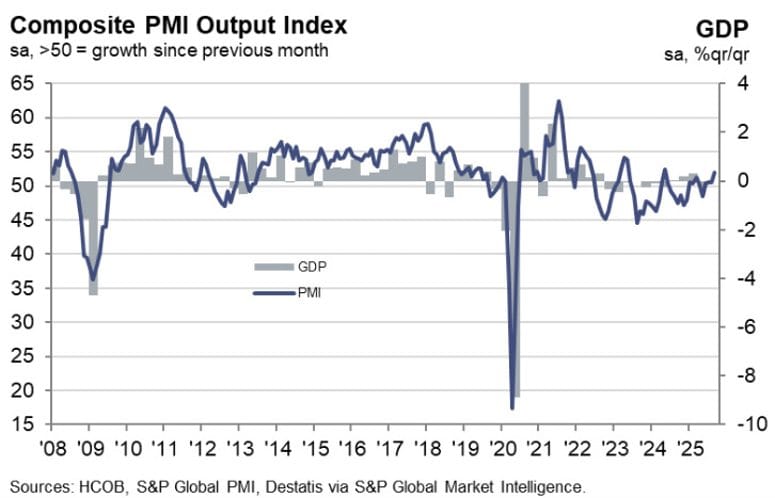
Commenting on the PMI data, Dr. Cyrus de la Rubia, Chief Economist at Hamburg Commercial Bank, said:
“At first glance, the PMI figures for September are encouraging. The service and manufacturing sectors have together seen a robust increase in output, and the pace of expansion is at its highest in sixteen months. However, there are some downsides. In the manufacturing sector, new orders fell in September, ending a three-month growth streak. And in the service sector, new business has shrunk again, albeit the decrease has softened a bit compared to the previous month. It therefore does not look as if output in the private sector will rise sustainably in the coming months, unless demand revives.
“Cost inflation in the service sector has risen for the second month in a row and is at an above-average level. Given the rather weak performance of this sector over the past twelve months, this is not only unusual but also a problem for the companies affected. This is because the sales difficulties are compounded by rising costs, which can only be passed on to customers to a limited extent. An important factor responsible for these cost increases is likely to be the demographic shortage of skilled workers, which makes staff and human resource planning more expensive.
“Service providers are gradually responding to the slump in orders by cautiously reducing their workforces. Over the past two years, there have been repeated episodes where companies have reduced their employment, but for the most part, the number of jobs has increased. The fact that staff numbers have been cut for two months in a row does not necessarily herald a phase of job losses. However, there is increasing discussion about whether artificial intelligence is already making jobs redundant on a significant scale. It is therefore worth keeping a close eye on this development.”
France’s Services PMI Falls Deeper Into Contraction
France’s services sector weakened further in September, with the final HCOB Services PMI dropping to 48.5 from a preliminary 48.9 and below August’s 49.8.
The Composite PMI slipped to 48.1, also lower than the preliminary 48.4. Survey evidence points to soft demand dragging down activity. Competitive pressures forced some firms to cut prices, but the effect was minimal.
HCOB notes that:
“French politics is currently offering little support to businesses, as the ongoing political deadlock adds to uncertainty and undermines confidence. Amidst this turmoil, France’s private sector lost ground: the HCOB France Composite PMI weakened in September, with activity declining in both the manufacturing and service sectors.
“After approaching the growth threshold in August, the headline HCOB Services PMI experienced a renewed decline. The primary driver of this weak performance remains subdued demand conditions, as reflected in lower new order volumes. Domestically, political gridlock is likely contributing to clients hesitating in making spending decisions. Additionally, the challenging geopolitical and trade environment continues to weigh on foreign demand, as evidenced by the decline in export orders.
“Input price inflation continues, whereas output prices decreased in September. This suggests that companies’ margins might shrink, although cost pressures are subdued compared to historical levels. Interestingly, margin compression, coupled with restrained demand, has not yet translated into layoffs, as the employment index still indicated growth.”
Italy’s Services Activity Accelerates in September
Italy’s service economy expanded at a faster pace in September, with the HCOB Services PMI at 52.5 versus 51.5 expected and 51.5 in August.
The Composite PMI held steady at 51.7. Firms reported stronger business activity and new orders, though job creation slowed. Business confidence improved, suggesting optimism for the months ahead.
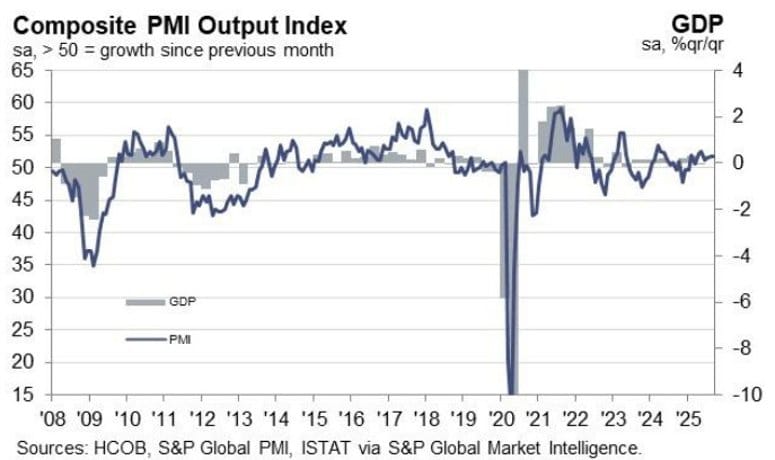
Commenting on the PMI data, Nils Müller, Junior Economist at Hamburg Commercial Bank, said:
“The latest HCOB PMI data paint a picture of divergence: while the services economy continues to expand, the manufacturing sector has slipped back into contraction. The composite PMI, which reflects the activities of both sectors in a single figure, signalled modest growth at the same pace as in the previous month. Yet this stability masks a growing imbalance between the sectors, raising questions about the sustainability of Italy’s private sector recovery.
“The services sector ended the third quarter on a strong note, with business activity rising at the fastest pace since May and new orders expanding at the quickest rate in nearly a year-and-a-half. Firms reported improving domestic demand, but export orders continued to decline amid muted European demand and geopolitical uncertainty. Employment rose for the eighth consecutive month, albeit at a slower pace, and backlogs of work were reduced further.
“Cost pressures remained elevated in September, with service providers citing rising wages – often linked to collective agreements – alongside higher energy, rent and commodity costs. Although the pace of output price inflation eased to the weakest level in ten months, charges continued to rise, extending the sequence of monthly increases to four years. Some companies reported offering discounts to support demand, suggesting that margin pressures are beginning to bite.
“Sentiment among service companies improved slightly, supported by expectations of further gains in new business and plans to expand service offerings. While confidence remains below the historical average, some firms anticipate a boost from major events such as the 2026 Winter Olympics in Milano Cortina. Overall, the outlook for the Italian economy hinges on whether services can maintain momentum in the face of persistent cost inflation and external headwinds, and whether manufacturing can stabilise to support a more balanced recovery.”
Italy Retail Sales Slip in August
Italy’s retail sales edged down 0.1% in August, missing expectations for flat growth. July’s figure was unchanged at 0.0%.
Year-over-year, sales rose 0.5%, slower than July’s 1.8%. Over the three months to August, retail sales rose 0.8% in value and 0.3% in volume.
Comparing with August 2024:
- Large-scale distribution sales climbed 2.5%.
- Small-scale retail fell 2.2%.
- Non-store sales dropped 2.6%.
- Online sales jumped 6.1%.
The data show resilience in digital retail but continued weakness among smaller physical retailers.
Spain’s Services Sector Outperforms in September
Spain’s services sector continued to drive growth in September, with the HCOB Services PMI coming in at 54.3, well above expectations of 53.0 and up from August’s 53.2.
The Composite PMI rose slightly to 53.8, compared to 53.7 previously. Growth was underpinned by strong new business inflows, though rising input costs remained a challenge. Service providers responded by raising selling prices, reflecting persistent inflationary pressure.
HCOB notes that:
“The Spanish economy is skilfully navigating global challenges, staying on a growth trajectory. Compared to the previous month, Spain’s private sector slightly accelerated its pace of growth, indicated by the HCOB Composite PMI posting at 53.8 in September after 53.7 in August. Sector-wise, growth momentum in manufacturing softened somewhat, whereas the service sector gained momentum.
“In September, the service sector sailed ahead with confidence, buoyed by robust demand and a surge in new business. Companies reported smooth progress in attracting fresh clients, keeping the momentum firmly on course. The only cloud on the horizon remains a softer dynamic in foreign export business, largely due to a slowdown in tourism, as anecdotal evidence shows. This appears to be linked to the broader European environment, with political deadlock in France likely dampening consumer sentiment there, a trend that may be spilling over to its southwestern neighbour.
“Looking to the horizon, Spanish service providers remain upbeat about the months ahead. Many survey participants anticipate a pickup in activity, attributing their confidence to encouraging demand forecasts, strategic business expansions, and the rollout of new service offerings. This forward-looking sentiment is mirrored in the labour market, where hiring intentions remain solid. Additionally, a rise in backlogged work suggests that capacity is being stretched – potentially fuelling further demand for staff as firms strive to keep pace, but also a factor contributing to persistently elevated cost pressures as firms navigate the challenge of scaling up.”
UK September Final Services PMI Slips to 50.8
The UK’s services sector slowed further in September, with the final S&P Global Services PMI coming in at 50.8—below the preliminary 51.9 and sharply down from 54.2 in August.
The final Composite PMI registered 50.1, also below the preliminary 51.0 and prior 53.5. Key findings show weaker growth in output and new orders, accelerated job losses, and continued strong input cost inflation.
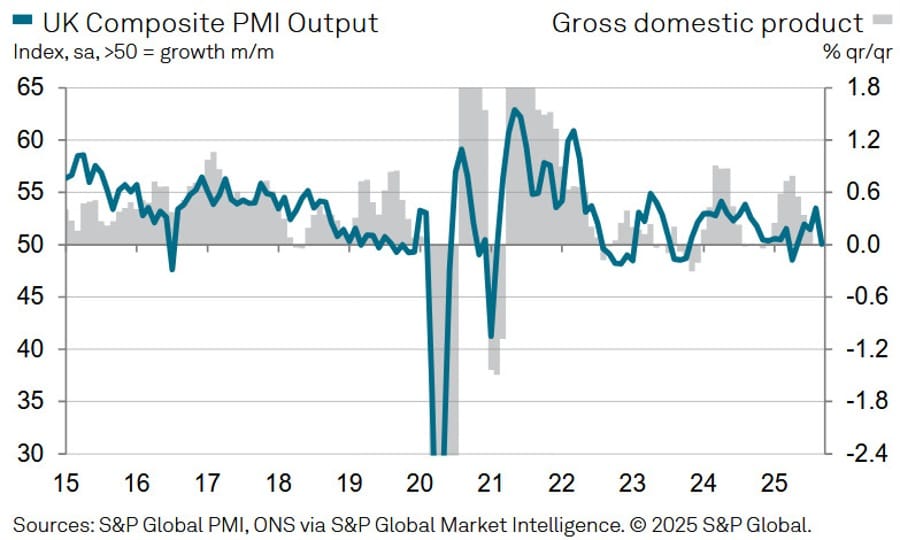
Tim Moore, Economics Director at S&P Global Market Intelligence, said:
“UK service providers experienced a disappointing end to the third quarter as weak consumer confidence, delays to business spending decisions and falling exports all weighed on demand. Business activity expansion hit a five-month low, while new order gains were much softer than the 11-month high seen in August.
“Consequently, this summer’s acceleration in output growth is now looking like a flash in the pan as elevated political and economic uncertainty has reasserted itself as a constraint on service sector performance. Many survey respondents suggested that corporate clients had deferred spending decisions until after the Autumn Budget, while households were also hesitant about major purchases.
“Outside of the UK, service providers were unable to escape challenging market conditions. Total new work from abroad returned to contraction territory in September. Lacklustre demand across Europe was a common theme reported by survey respondents.
“Another round of job cuts followed in the wake of the subdued service sector performance during September, which marked 12 months of falling employment. This was accompanied by softer growth projections for the year ahead and slightly weaker cost pressures. These signals of softening labour market conditions and easing inflationary pressures are likely to provide support to the more dovish shift in the policy debate at the Bank of England.”
Lagarde says ‘we are in a good place’ on rates
- European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde suggests a pause
- “We are in a good place and we have to make sure that we stay in that good place”
- “There is no preset pace”
- “We have done a lot already.”
- “We don’t expect significant movement up or down in relation to inflation”
- “what I would say is that the euro area in general has shown more resilience than anticipated.”
ECB’s Wunsch: We are in a good place
- Comment from the ECB policymaker, Pierre Wunsch
Asia-Pacific & World News
China Floats US Factory Build in Trade Talks
Beijing has raised the prospect of constructing large-scale factories in the United States as part of trade negotiations, according to a Bloomberg report. The proposal, first surfaced in Madrid last month, was pitched as a way to reduce tariffs on Chinese exports.
China has reportedly suggested investing as much as $1 trillion, a dramatic leap compared to the $2.1 billion invested in the first half of 2025.
If such a deal materializes, it could reshape global trade dynamics, influence inflation expectations, and spur a scramble for resources as supply chains are restructured.
Nvidia’s U.A.E. Chip Deal Stalls Over Investment and Security Concerns
A high-profile deal to deliver Nvidia’s advanced AI chips to the United Arab Emirates is in limbo, five months after being announced. The agreement, hailed as a landmark in Washington’s push to expand strategic tech exports, has been bogged down by delays in Emirati investment commitments and security concerns over China ties.
The May deal promised the U.A.E. several hundred thousand Nvidia chips annually in exchange for Emirati investment in the United States. Those investments have yet to materialize, leaving Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick unwilling to grant export approval.
Adding to the holdup are national security worries. U.S. officials fear that the U.A.E.’s close relationship with China could indirectly funnel sensitive chips into Beijing’s AI sector.
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang and White House AI envoy David Sacks had championed the deal as a showcase for Washington’s export strategy and as a bulwark against China in the global AI race. Instead, the stalled agreement is raising questions about the U.S.’s ability to use chip exports as a geopolitical tool.

Australia’s September PMIs Signal Slower Growth, Still in Expansion
All three of Australia’s S&P Global Purchasing Manager’s Indexes (PMIs) fell in September but remained above the 50.0 threshold, marking continued—though softer—expansion.
- Manufacturing PMI: 51.4, down from 53.0 in August. Conditions improved for a ninth straight month, though at a slower pace.
- Services PMI: 52.5, compared to 55.8 in August. Expansion extended to 20 months but was the weakest since June.
- Composite PMI: 52.4, down from 55.5. This was also the weakest since June.
Overall, September’s readings show that while the economy remains in growth mode, momentum has clearly eased.
Japan’s August Unemployment Rate Edges Up to 2.6%
Japan’s labor market showed mixed results in August. The unemployment rate rose to 2.6%, missing forecasts for 2.4% and up from 2.3% in July. Meanwhile, the jobs-to-applicants ratio slipped to 1.20, below both expectations and the prior 1.22 reading.
The figures suggest some cooling in hiring momentum even as Japan continues to face labor shortages in key sectors.
Japan’s LDP Faces Pivotal Leadership Choice: Takaichi vs. Koizumi
Japan is preparing for a critical leadership contest within the ruling Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), where the outcome could reshape both domestic policy and the nation’s global standing. With Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba stepping aside following repeated electoral setbacks, the party is weighing a generational and ideological shift.
The race centers on two figures: 64-year-old Sanae Takaichi, a staunch conservative and longtime advocate of “Abenomics,” and 44-year-old Shinjiro Koizumi, son of former prime minister Junichiro Koizumi, who campaigns on reformist themes. Also in contention is Chief Cabinet Secretary Yoshimasa Hayashi, 64, seen as a steady hand continuing Ishiba’s more cautious approach. In total, five candidates are standing.
Takaichi has strong grassroots backing and is calling for a state-driven spending plan designed to double the size of Japan’s economy within ten years. She has also suggested reopening negotiations on Japan’s $550 billion investment deal with the United States. Koizumi, more popular among lawmakers, has pledged tax relief to reduce household burdens while pushing for fiscal discipline. Hayashi represents the continuity option, favoring stability over radical change.
The first round of voting takes place Saturday. If no candidate secures a majority, a runoff will be held later the same day. In that scenario, Koizumi and Hayashi could gain an edge, as influence shifts away from rank-and-file members toward lawmakers. Whoever emerges victorious will inherit a weakened party and an economy struggling with sluggish growth.
Markets are watching closely. A Koizumi win could reduce political uncertainty and open the door to a Bank of Japan rate hike in October. Takaichi, by contrast, signals she would prefer to keep monetary policy loose.
BOJ Governor Ueda: Staying Accommodative Amid Global Risks
Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda reaffirmed his commitment to maintaining a loose monetary stance, stressing that the central bank must support corporate activity while navigating rising global risks.
Ueda noted signs that Japanese households are cutting back spending due to higher food prices, requiring vigilance. While overall corporate earnings remain strong, some manufacturers are already feeling the pinch from tariffs, as shown in recent export and production data.
He said the BOJ stands ready to raise rates if forecasts for steady improvement hold, but he cautioned that tariffs, a slowing U.S. economy, and fragile wage growth add uncertainty. “We will judge without preconceptions whether the economy and prices are moving as projected,” Ueda stated.
Japan’s growth is expected to slow in the near term before strengthening as overseas economies recover. However, Ueda emphasized that tariff policy—particularly the 15% U.S. import duty—creates global unpredictability that could weigh heavily on Japan’s outlook.
Other key points from Ueda’s remarks:
- U.S. job growth is losing momentum, which may signal pressure on profits, jobs, and incomes.
- Japan has not yet seen a broad spillover from U.S. tariffs, but the risk remains.
- Corporate wage-setting behavior could weaken if trade uncertainty persists.
- Business strategies will need to adapt to the agreed tariff environment, though the timing remains unclear.
Ueda concluded that sustaining an accommodative monetary environment is essential until Japan achieves durable growth and stable price momentum.
Japan finance minister Kato watching the impact from the US government shutdown with intense interest
Japan Finance Minister Kato:
- Watching with high interest, including the impact on financial markets and corporate economic activities from the U.S. government shutdown.
- Will explore potential steps to increase pressure on Russia over Ukraine.
- Aware we need to find ways to cut revenue for Russia.
- Not able to boost tariffs on countries importing Russian oil from perspective of compliance with international laws
Crypto Market Pulse
Bitcoin Nears Record High as ETF Inflows Surge
Bitcoin jumped 2.17% Friday to $123,171, briefly reaching $123,966, just below August’s all-time high of $124,517. Since last Friday’s low of $108,676, BTC has gained 13.6%.
ETF inflows (this week):
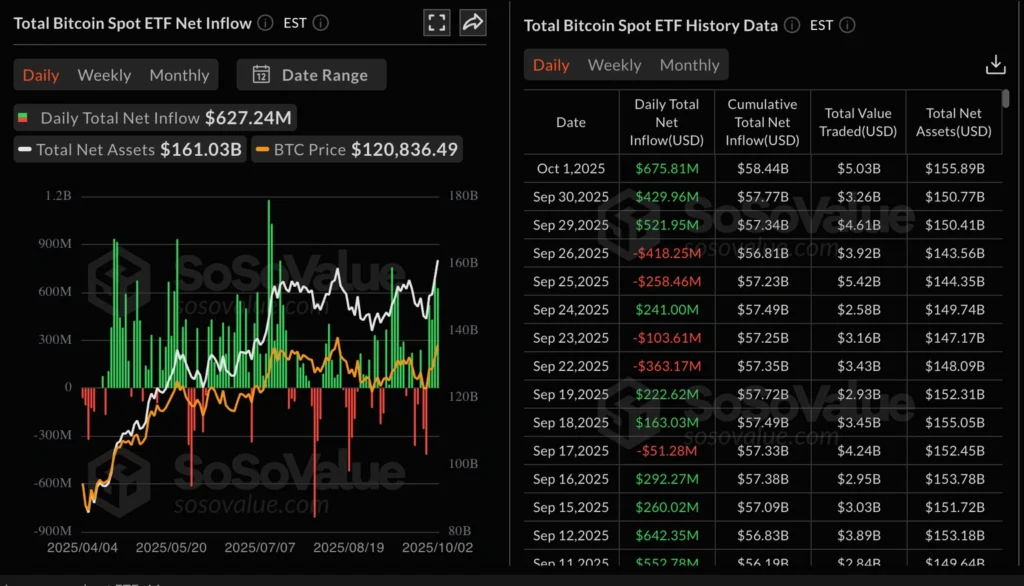
- Monday: $522M
- Tuesday: $430M
- Wednesday: $676M
- Thursday: $627M
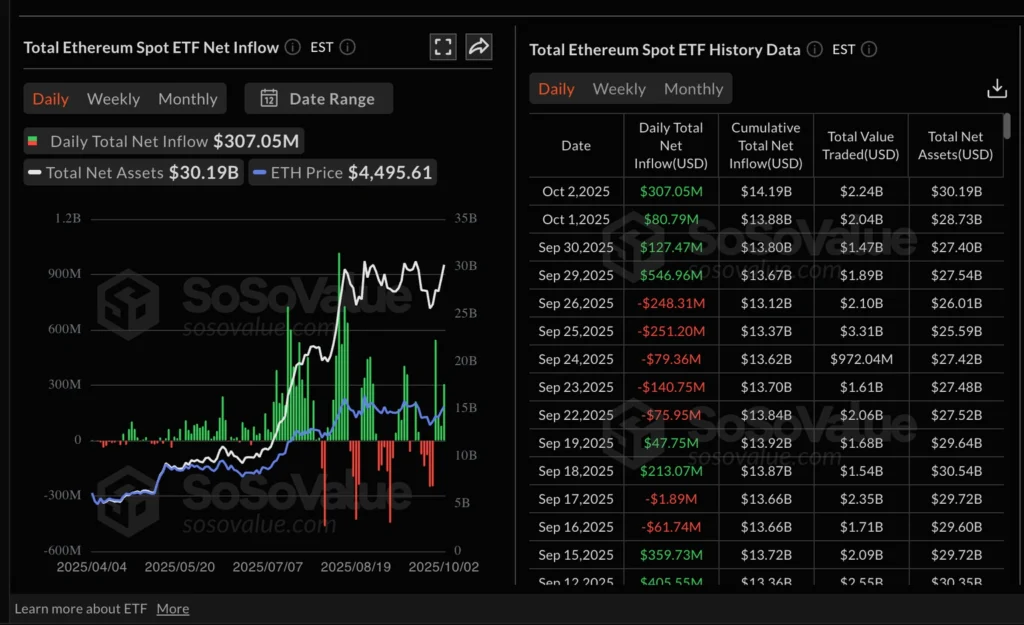
BlackRock’s IBIT led with $466M on Wednesday, followed by Fidelity ($87M) and Ark Invest ($45M). Notably, none of the 12 products saw outflows. Ethereum ETFs also saw steady demand, with $307M inflows on Thursday, led by BlackRock’s ETHA ($177M).
Sentiment has been buoyed by “Uptober” optimism, falling bond yields, and fading confidence in traditional currencies amid government shutdown risks.
Analyst forecasts:
- Citibank: Base $181K, bear $82K, bull $231K over 12 months
- Standard Chartered: $200K by end-2025, with a near-term break of $135K
A clear move above $124,517 would target $127,000 in the near term.
Chainlink Faces Selling Pressure as Whales Take Profits
Chainlink (LINK) fell 2% Friday toward $22.15, weighed down by profit-taking from whales and weakening derivatives activity.
On-chain trends:
- Whales booked profits on 84.98M LINK this week, aligning with 102 large transactions.
- Profit-taking has slowed slightly, with 88% of supply still in profit (up from 84.75% earlier in the week).
Derivatives signals:
- Open Interest dropped 3% to $1.32B, showing traders are cutting positions.
- Funding rates remain elevated at 0.0101%, suggesting demand for long exposure persists despite the pullback.
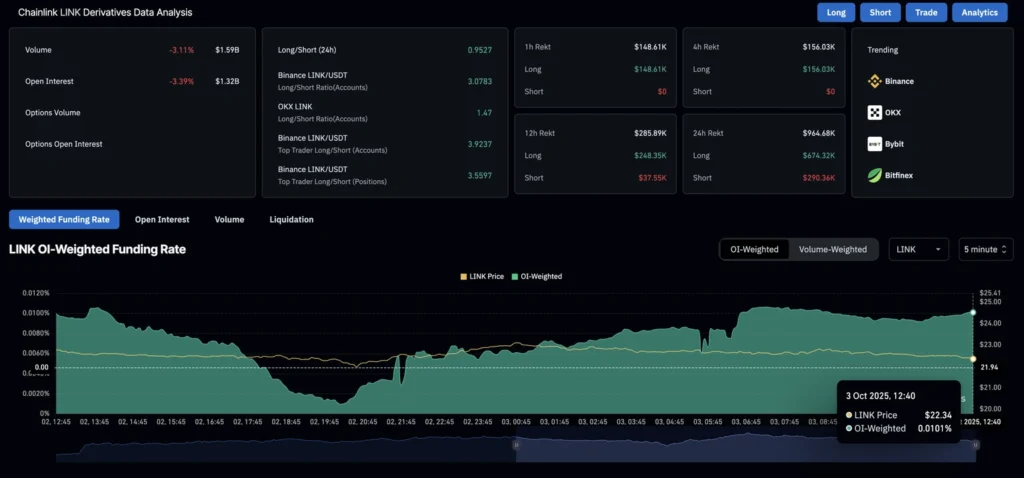
LINK remains within a symmetrical triangle on the daily chart, with downside risk if whale selling continues.
BNB Hits Record High on Exchange and Chain Growth
BNB surged above $1,100 Friday, entering record territory as Binance’s centralized exchange holdings and BNB Chain activity hit new peaks.
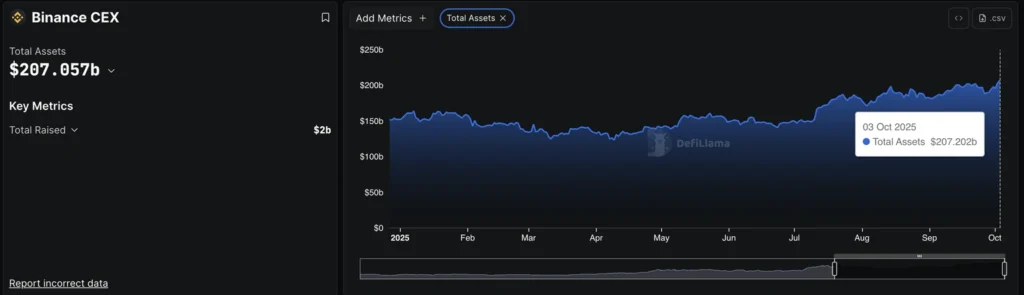
Exchange growth: Binance CEX assets reached $207B, a new record, signaling rising trading activity.
BNB Chain expansion:
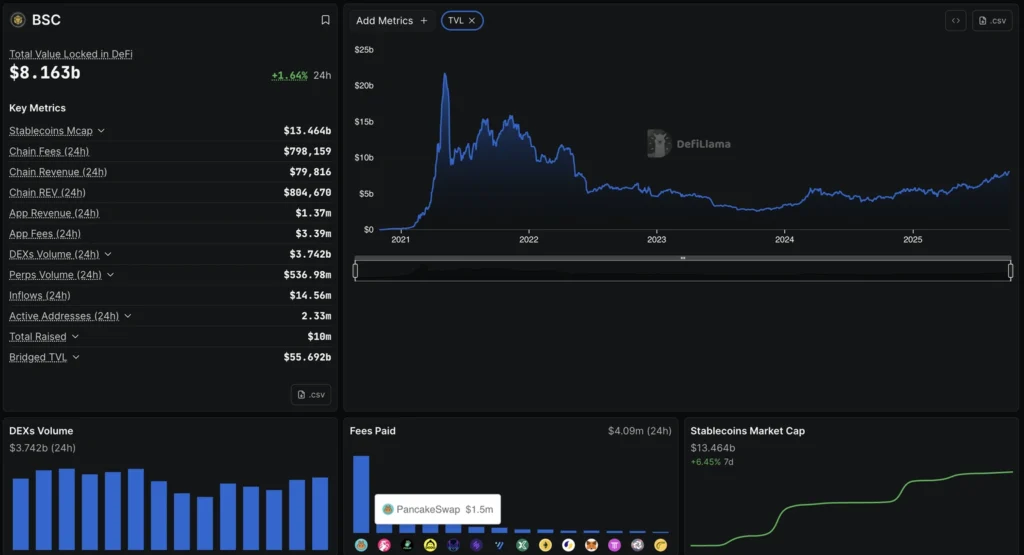
- Total Value Locked: $8.163B (4th largest DeFi chain)
- DEX volume: >$3B in four days, led by PancakeSwap fees of $1.51M in 24h
- Stablecoin supply: +6% in 24h to $13.46B
Plans for prediction markets on BNB Chain could boost further demand, positioning the network to challenge platforms like Polymarket. With strong fundamentals across both DeFi and centralized platforms, BNB’s bullish momentum looks supported.

XRP Holds $3.00 as Whales Add Exposure
Ripple’s XRP held steady above $3.00 on Friday after a two-day rally from September lows near $2.70. Traders eye a potential run toward July’s record high of $3.66 if momentum continues.
Whale activity:
- Wallets with 10M–100M XRP now hold 12.27% of supply, up from 12.06% (Sept 25).
- Wallets with 100M–1B XRP increased holdings to 14.6%, from 13.85% earlier this week.
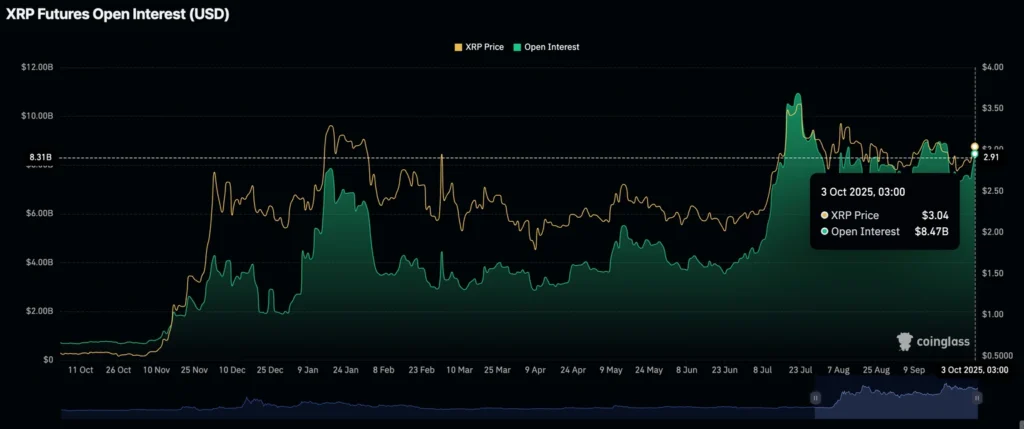
Derivatives markets also signal growing conviction: Open Interest in XRP futures rebounded to $8.47B, up from September’s low of $7.35B. The increase reflects rising engagement from both retail and institutional traders.
A daily close above $3.00 would reinforce bullish sentiment and raise the probability of a retest of all-time highs.
Pump.fun Extends Rally Above $0.0070
Pump.fun (PUMP) continued its rally on Friday, climbing above $0.0070 for a fourth straight day of gains, despite corrections in Bitcoin and Ethereum.
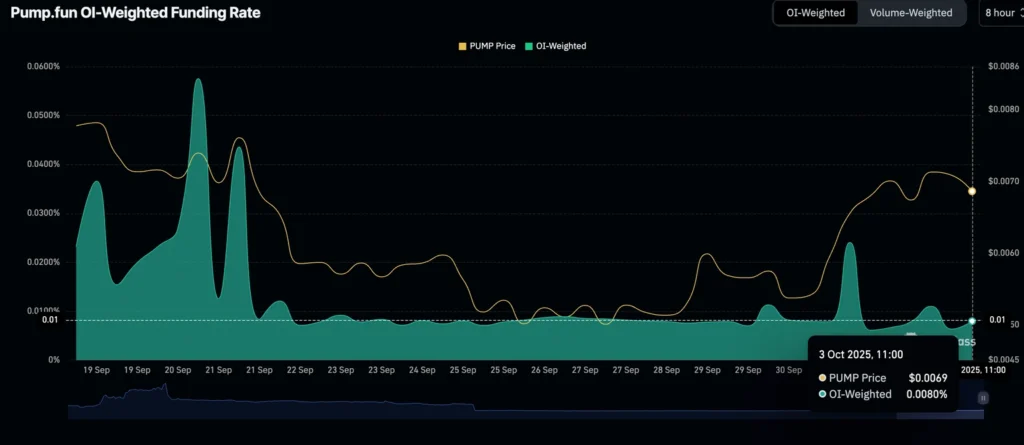
Derivatives support trend:
- Futures Open Interest rebounded to $866M after dipping to $626M on Sept. 26.
- Funding rates averaged 0.0080% on Friday, suggesting more traders are taking long positions.
On the 4-hour chart, a Golden Cross pattern confirms a strong technical backdrop. Rising OI alongside price gains suggests confidence is building among traders, reinforcing momentum for a potential breakout toward new highs.
Meme Coins See Mixed Moves as Dogecoin Forms Golden Cross
Meme coin activity slowed Friday after two days of gains, but derivatives data shows retail traders remain active.
Futures Open Interest (24h change):
- Dogecoin (DOGE): $4.61B (+4%)
- Pepe (PEPE): $639.50M (+4%)
- Shiba Inu (SHIB): $202.55M (steady)
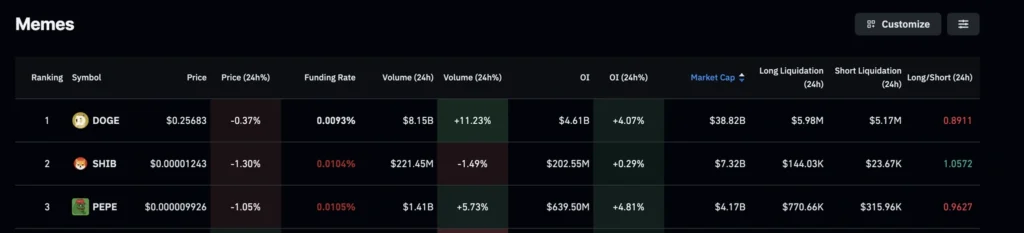
Dogecoin: DOGE slipped 2% to $0.2500, consolidating after hitting $0.26418 earlier. RSI cooled to 65, while MACD neared a bearish crossover. Key supports lie at $0.2500 and the 100-EMA at $0.24423. Still, a 50/200 EMA Golden Cross suggests the broader trend favors bulls. Upside target remains $0.28879.
Shiba Inu: SHIB eased before the $0.00001277 resistance, holding above its 100-EMA. RSI sits at 58, showing stable buying pressure. Supports are seen at $0.00001219 and $0.00001209.
Pepe: PEPE retreated from its 50-day EMA at $0.00001032, trading 2% lower. RSI recovered to 48, while MACD hints at a bullish crossover. A retest of $0.00000887 support remains a risk.

The Day’s Takeaway
North America
U.S. Equities
- Dow Jones: 46,758.28 (+238.56, +0.51%) – record close
- S&P 500: 6,715.79 (+0.44, +0.01%) – record close
- Nasdaq: 22,780.51 (-63.54, -0.28%) – pullback after record
- Russell 2000: 2,476.17 (+17.69, +0.72%)
Weekly gains: Dow +1.10%, S&P +1.09%, Nasdaq +1.32%, Russell 2000 +1.72%
Sector performance:
- Strong: Healthcare +6.82% (best since June 2022), Utilities +2.39%, IT +2.25%
- Weak: Energy -3.34%, Communication Services -2.10%, Consumer Discretionary -0.81%
Federal Reserve
- Williams: Public understanding improves policy effectiveness; robust policy must adapt to constant economic change.
- Goolsbee: Cautious on front-loading cuts; labor market still stable but risks rising.
- Miran: Sees significant disinflation in services; warns against backward-looking neutral rate estimates.
- Jefferson: Expects disinflation to resume in 2026; immigration decline limiting unemployment rise.
- Logan: Sees modestly restrictive stance; concerned about prolonged tariff impacts and sticky services inflation.
Economic Data
- ISM Services PMI (Sept): 50.0 vs 51.7 expected (prior 52.0) – flatline between expansion and contraction.
- S&P Global Final Services PMI (Sept): 54.2 vs 53.9 prelim – growth still evident, but slower demand.
- Labor market data unavailable due to government shutdown (jobless claims, NFP).
Rig Counts (Baker Hughes)
- U.S.: 549 rigs (unchanged) – oil -2, gas +1, misc +1. Down 36 YoY. Offshore +1 on week.
- Canada: 190 rigs (unchanged). Down 33 YoY.
Canada – Policy & Trade
- PM Mark Carney to visit Washington Oct 7 for Trump meeting.
- Focus: review of CUSMA, economic & security ties.
- Market view: low expectations for major trade deal announcement.
Commodities
Gold
- Price: $3,882 (+0.70%) – near record high $3,896.
- 7th straight weekly gain as shutdown extends to day 3.
- Fed’s dovish tone + data blackout sustaining haven demand.
Silver
- Price: $47.10 – holding just below $48 peak.
- Bullish channel intact; resistance $48.70 / $50.
- RSI overbought but momentum intact above $46.
Oil
- WTI Crude: $60.88 (+$0.40, +0.66%) Friday close.
- Weekly: -6.61% (-$4.31), sharpest drop since June 23.
- OPEC+ expected to hike output Nov: 140K–411K bpd. Saudi pushing for higher, Russia cautious.
- Closed below $61.45–$61.94 swing zone = bearish technicals.
OPEC+
- Saudi Arabia pushing for aggressive hikes (274K–548K bpd).
- Russia prefers smaller increase (~137K bpd).
- Spare capacity concerns remain.
Europe
Equities (Friday close)
- Euro Stoxx 50: 5,656.90 (+0.03%, weekly +2.79%)
- Germany DAX: 24,378.81 (-0.18%, weekly +2.69%)
- France CAC 40: 8,081.55 (+0.31%, weekly +2.68%)
- UK FTSE 100: 9,491.24 (+0.67%, weekly +2.22%) – record close
- Spain IBEX 35: 15,585.10 (+0.57%, weekly +1.53%) – strongest since 2007
- Italy FTSE MIB: 43,258.10 (+0.42%, weekly +1.43%)
Tone: Broad-based weekly strength across Europe despite DAX’s small Friday dip.
Asia
Trade & Policy
- China: Floated $1T U.S. factory investment proposal in exchange for tariff relief. Could reshape inflation and GDP outlooks if realized.
Crypto
Bitcoin (BTC)
- Price: $123,171 (+2.17%), high $123,966 – just below ATH $124,517.
- Weekly gain: +13.6% (low $108,676 last week).
- ETF inflows: $2.26B across week. BlackRock IBIT led.
- Forecasts: Citi $181K base, $231K bull; Standard Chartered $200K 2025 target.
- Near term: Break of $124,517 would target $127K.
BNB
- Price: >$1,100, new record.
- Exchange: Binance CEX assets $207B (record).
- BNB Chain: $8.16B TVL (4th in DeFi), $3B+ DEX volume in 4 days.
- Stablecoin supply +6% in 24h.
XRP
- Price: $3.00 support holding.
- Whales: Large wallets increased holdings to 26.87% of supply.
- Open Interest: $8.47B (up from $7.35B Sept low).
- Close above $3.00 opens path toward ATH $3.66.
Pump.fun (PUMP)
- Price: $0.0070, 4th straight day of gains.
- Futures OI: $866M (up from $626M Sept 26).
- Golden Cross on 4H chart confirms bullish structure.
Meme Coins
- DOGE: $0.2500 (-2%), consolidating; Golden Cross intact. Target $0.2888.
- SHIB: Holding above 100-EMA near $0.00001219.
- PEPE: -2%, rejected at 50-day EMA. RSI recovering, MACD bullish setup.
Chainlink (LINK)
- Price: $22.15 (-2%).
- Whales booked profits on ~85M LINK this week.
- OI down 3% to $1.32B, but funding still positive.
- Still in symmetrical triangle – watch for breakout/breakdown.